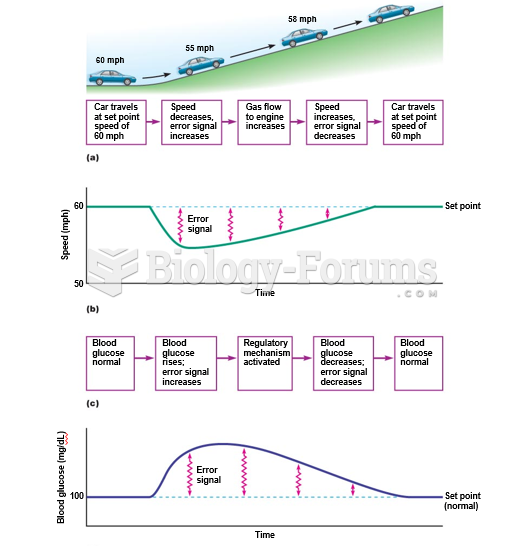
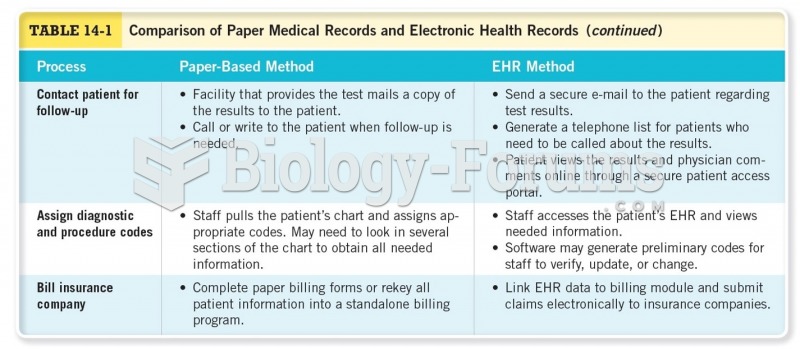
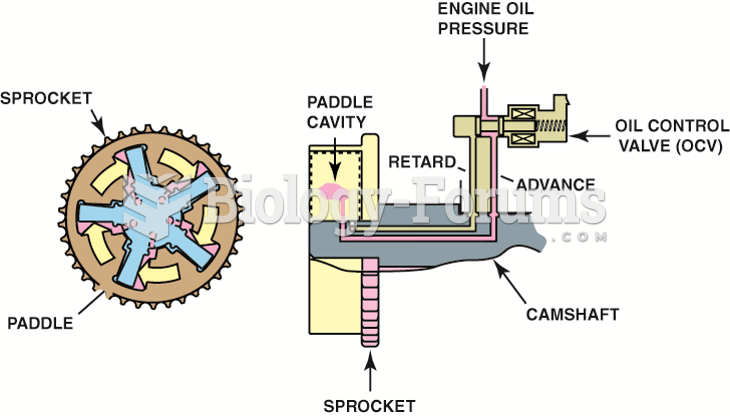
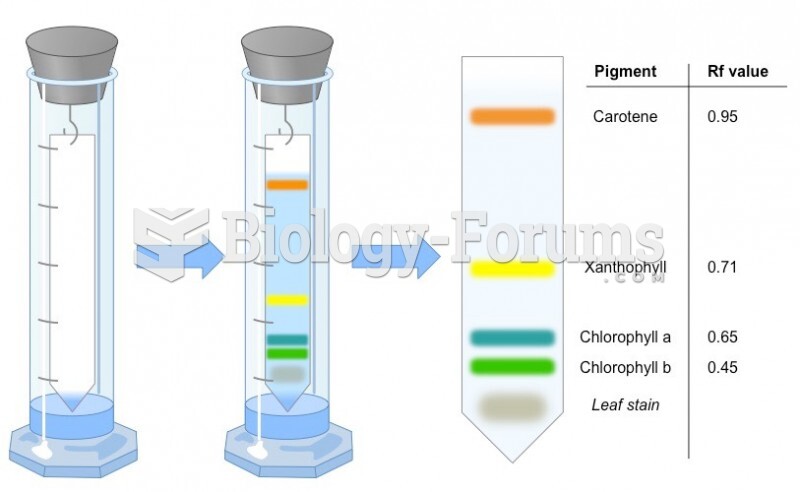
|
|
|
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.
Despite claims by manufacturers, the supplement known as Ginkgo biloba was shown in a study of more than 3,000 participants to be ineffective in reducing development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.