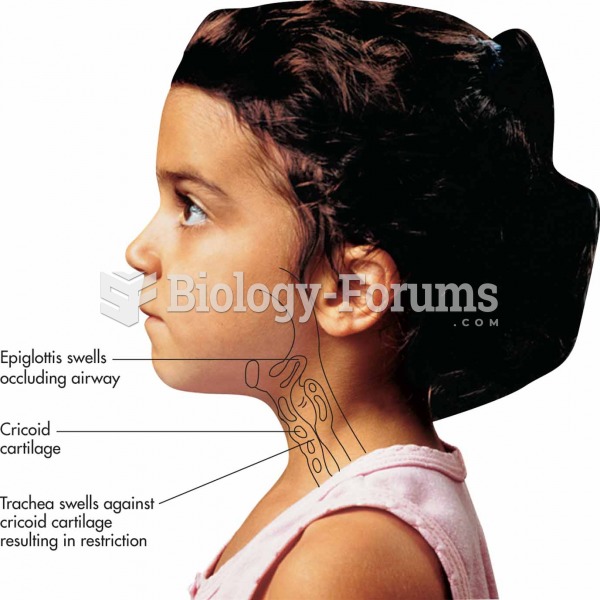
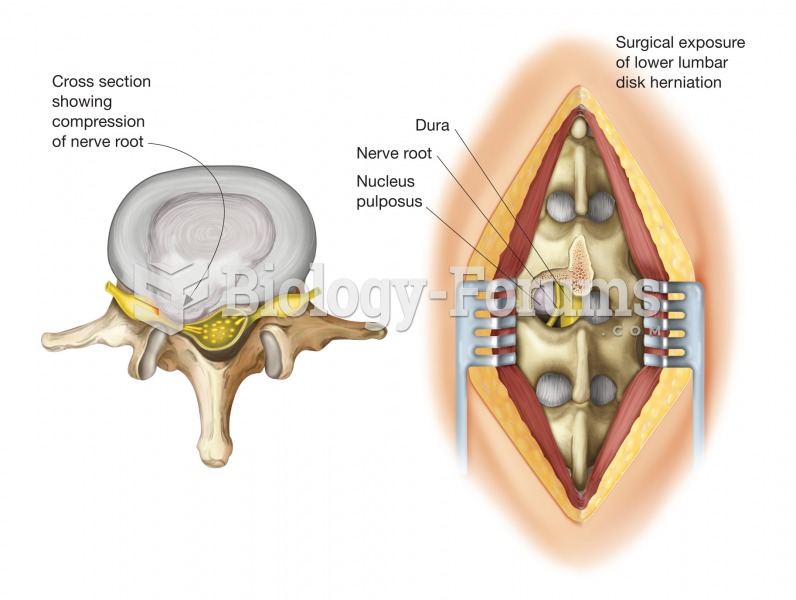
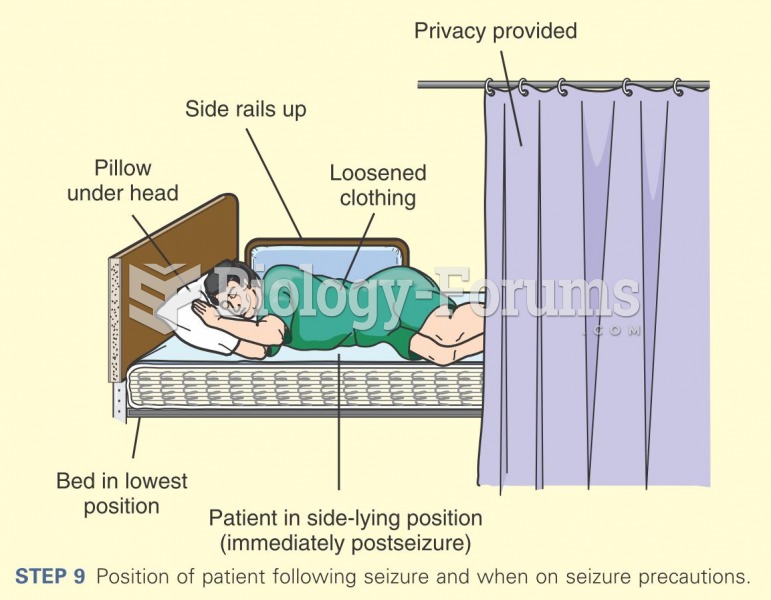
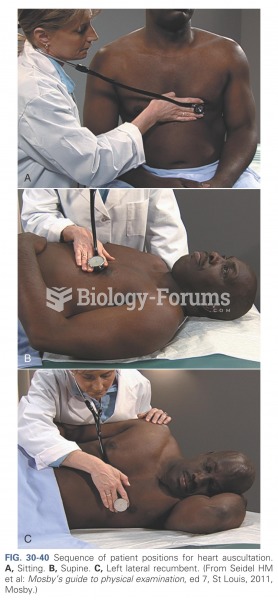
|
|
|
On average, someone in the United States has a stroke about every 40 seconds. This is about 795,000 people per year.
Women are 50% to 75% more likely than men to experience an adverse drug reaction.
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
The National Institutes of Health have supported research into acupuncture. This has shown that acupuncture significantly reduced pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, when used as a complement to conventional therapies.