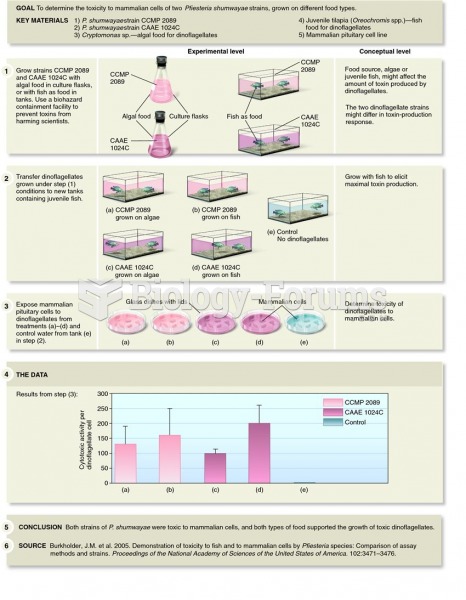
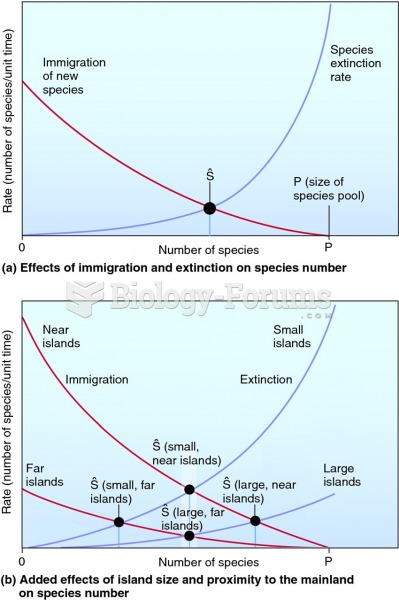
Answer to Question 1ANS: 2
Swanson's theory of caring defines five components of caring: knowing, being with, doing for, enabling, and maintaining belief (see Chapter

. These components provide a foundation of knowledge for the direction and delivery of caring nursing practice. This theory provides a basis for identifying and testing nurse caring behaviors to determine if caring improves client health outcomes. Offering to stay with the client is an intervention directly reflected of being with' the client. Efficiency is a component of caring but it is not the best option available because it is not exclusively directed toward Swanson's theory. Administering pain medication promptly reflects effective nursing care as well as a client's right. It is a component of caring but it is not the best option available because it is not exclusively directed towards Swanson's theory. Effective nurs-ing care and caring for the family is important, but it is not the best option available because it is not directed towards the client.
Answer to Question 2ANS: 4
If a nurse uses Orem's theory in practice, the nurse assesses and interprets the data to determine the client's self-care needs, self-care deficits, and self-care abilities in the management of a dis-ease. The theory then guides the design of individualized nursing interventions.
While the other interventions are appropriate and will ultimately affect effective client self-care/management of the diabetes, they are not the correct option because they are not direct-ly involved in determining client self-care needs.