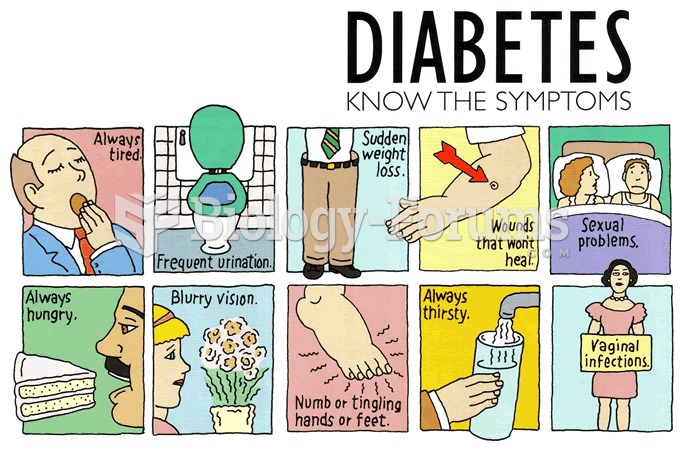
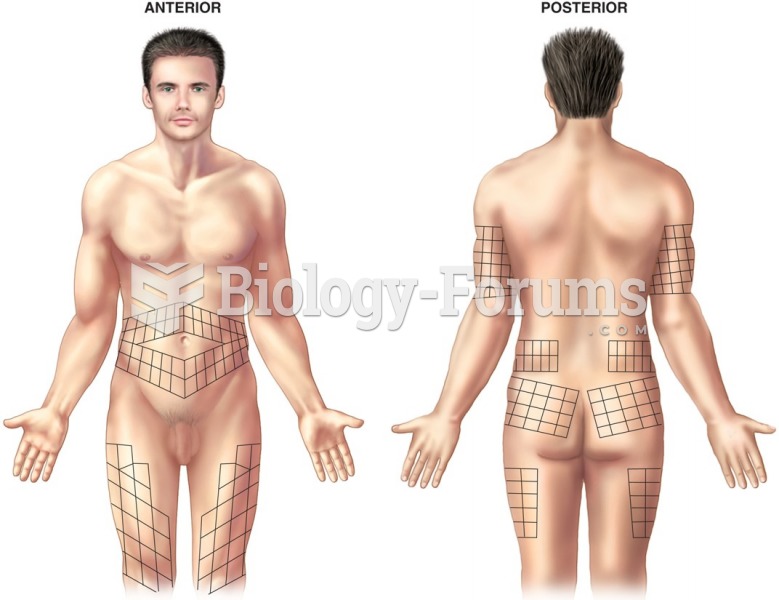
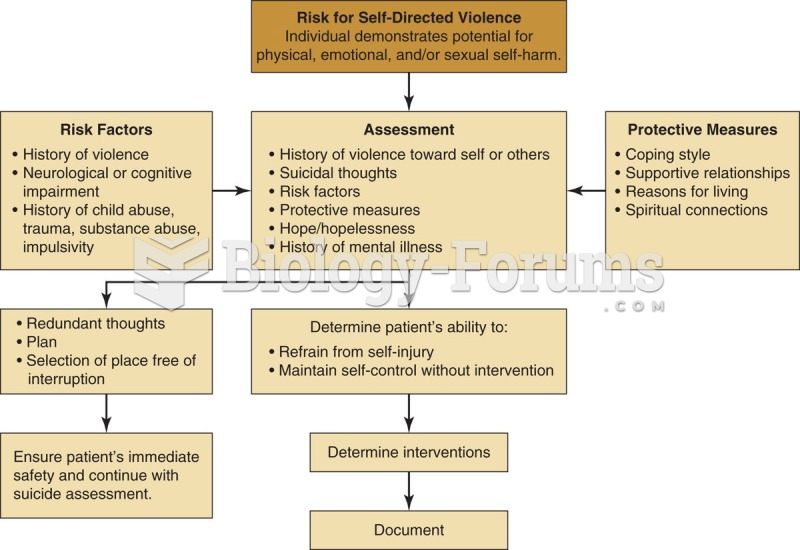
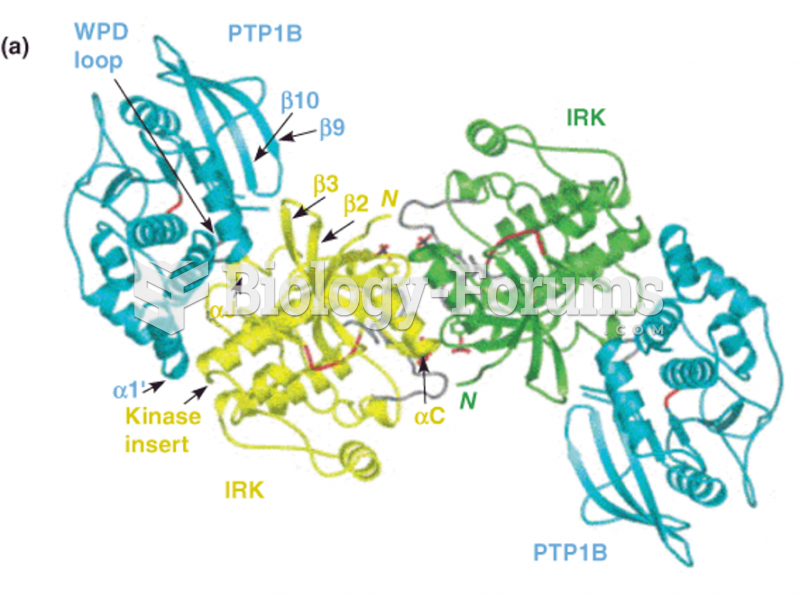
|
|
|
The FDA recognizes 118 routes of administration.
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Though newer “smart” infusion pumps are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, they cannot prevent all programming and administration errors. Health care professionals that use smart infusion pumps must still practice the rights of medication administration and have other professionals double-check all high-risk infusions.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.