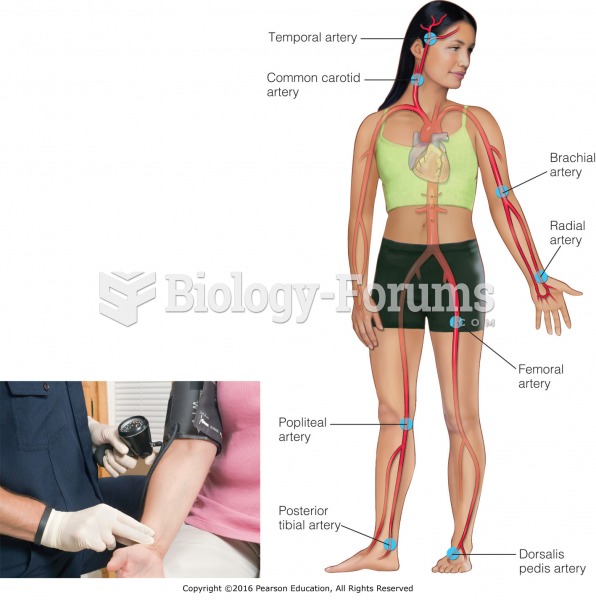
|
|
|
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
The human body produces and destroys 15 million blood cells every second.
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.
Asthma occurs in one in 11 children and in one in 12 adults. African Americans and Latinos have a higher risk for developing asthma than other groups.
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.
 Establishing a caring and trusting relationship helps the client come to terms with a terminal illne
Establishing a caring and trusting relationship helps the client come to terms with a terminal illne
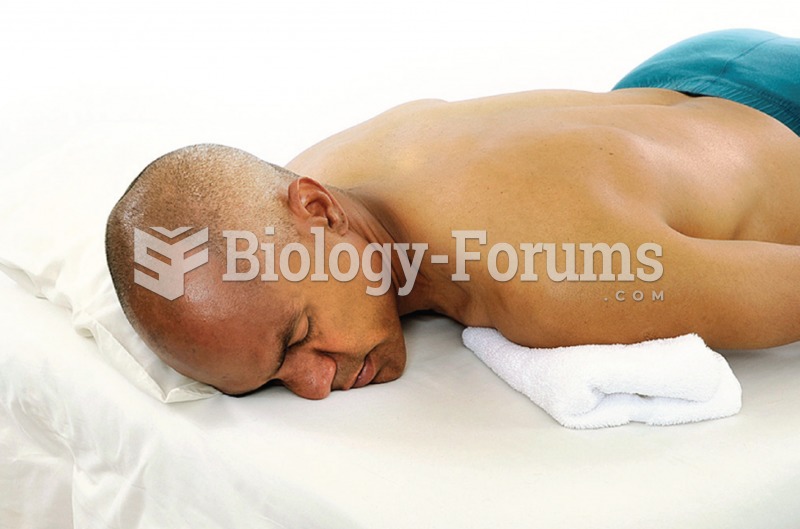 To reduce stress on your client’s neck when the head is turned, put a towel under the shoulder and ...
To reduce stress on your client’s neck when the head is turned, put a towel under the shoulder and ...