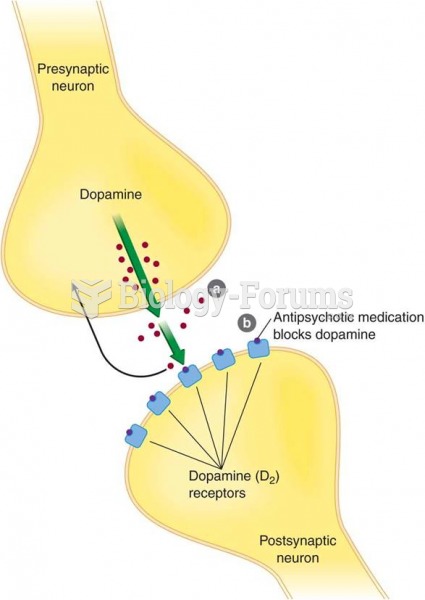
Answer to Question 1
3
Rationale 1: Crystalloids increase volume in the system. Cardiogenic shock is related to the force of myocardial contraction.
Rationale 2: Colloids increase volume in the cardiovascular system. Cardiogenic shock is related to the force of myocardial contraction.
Rationale 3: Inotropic drugs, also called cardiotonic drugs, have the potential to reverse the cardiac symptoms of shock by increasing the force of myocardial contraction.
Rationale 4: Vasopressors increase the blood return to the heart but do not increase the force of myocardial contraction.
Global Rationale: Cardiogenic shock is usually noted with a history of cardiac disease or inadequate force of myocardial contraction. Inotropic drugs, also called cardiotonic drugs, have the potential to reverse the cardiac symptoms of shock by increasing the force of myocardial contraction.
Answer to Question 2
1, 2, 4
Rationale 1: A number of other drugs are useful in treating symptoms of anaphylaxis. Oxygen is usually administered immediately. Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) may be administered IM or IV to prevent additional release of histamine. A bronchodilator such as albuterol (Ventolin, Proventil) is sometimes administered by inhalation to relieve the acute shortness of breath caused by histamine release. Corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone may be administered to dampen the inflammatory response. Corticosteroids may be administered for 24 hours or longer to prevent the possibility of delayed anaphylactic reactions.
Rationale 2: A number of other drugs are useful in treating symptoms of anaphylaxis. Oxygen is usually administered immediately. Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) may be administered IM or IV to prevent additional release of histamine. A bronchodilator such as albuterol (Ventolin, Proventil) is sometimes administered by inhalation to relieve the acute shortness of breath caused by histamine release. Corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone may be administered to dampen the inflammatory response. Corticosteroids may be administered for 24 hours or longer to prevent the possibility of delayed anaphylactic reactions.
Rationale 3: Aspirin (ASA) is not given to treat anaphylaxis.
Rationale 4: A number of other drugs are useful in treating symptoms of anaphylaxis. Oxygen is usually administered immediately. Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) may be administered IM or IV to prevent additional release of histamine. A bronchodilator such as albuterol (Ventolin, Proventil) is sometimes administered by inhalation to relieve the acute shortness of breath caused by histamine release. Corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone may be administered to dampen the inflammatory response. Corticosteroids may be administered for 24 hours or longer to prevent the possibility of delayed anaphylactic reactions.
Rationale 5: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is not given to treat anaphylaxis.
Global Rationale: A number of other drugs are useful in treating symptoms of anaphylaxis. Oxygen is usually administered immediately. Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) may be administered IM or IV to prevent additional release of histamine. A bronchodilator such as albuterol (Ventolin, Proventil) is sometimes administered by inhalation to relieve the acute shortness of breath caused by histamine release. Corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone may be administered to dampen the inflammatory response. Corticosteroids may be administered for 24 hours or longer to prevent the possibility of delayed anaphylactic reactions. Aspirin (ASA) and acetaminophen (Tylenol) are incorrect because they not given to treat anaphylaxis.