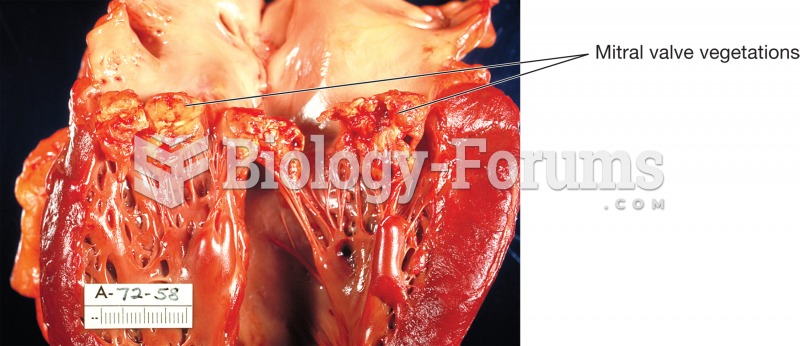
|
|
|
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).
To maintain good kidney function, you should drink at least 3 quarts of water daily. Water dilutes urine and helps prevent concentrations of salts and minerals that can lead to kidney stone formation. Chronic dehydration is a major contributor to the development of kidney stones.
More than 50% of American adults have oral herpes, which is commonly known as "cold sores" or "fever blisters." The herpes virus can be active on the skin surface without showing any signs or causing any symptoms.
Sperm cells are so tiny that 400 to 500 million (400,000,000–500,000,000) of them fit onto 1 tsp.
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.