This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
On average, someone in the United States has a stroke about every 40 seconds. This is about 795,000 people per year.
Did you know?
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Did you know?
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Did you know?
The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 and occurred in Boston. A kidney from an identical twin was transplanted into his dying brother's body and was not rejected because it did not appear foreign to his body.
Did you know?
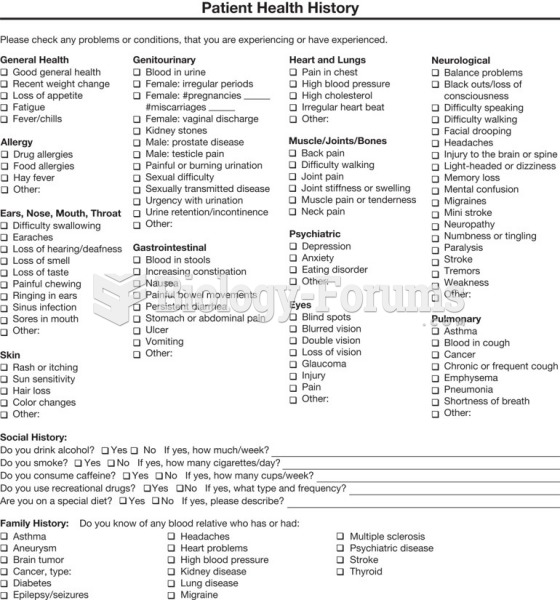
Medication errors are more common among seriously ill patients than with those with minor conditions.