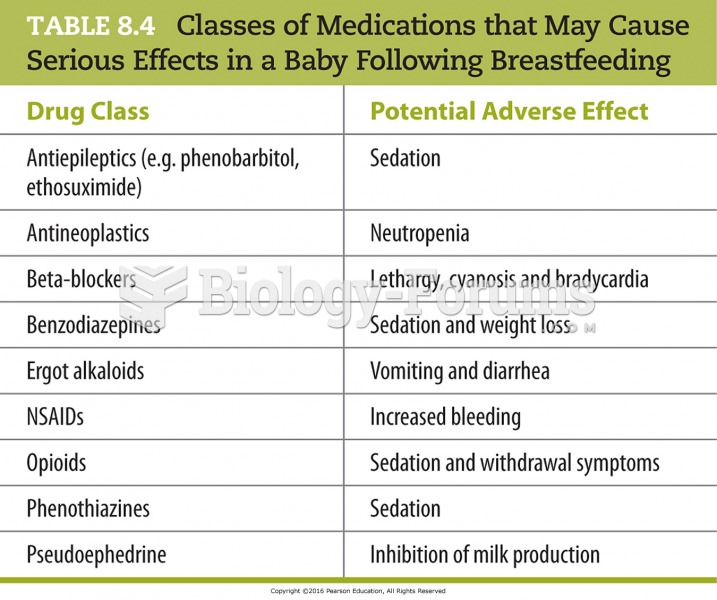
|
|
|
When Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the first mercury thermometer, he called "zero degrees" the lowest temperature he was able to attain with a mixture of ice and salt. For the upper point of his scale, he used 96°, which he measured as normal human body temperature (we know it to be 98.6° today because of more accurate thermometers).
The cure for trichomoniasis is easy as long as the patient does not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours. Just a single dose of medication is needed to rid the body of the disease. However, without proper precautions, an individual may contract the disease repeatedly. In fact, most people develop trichomoniasis again within three months of their last treatment.
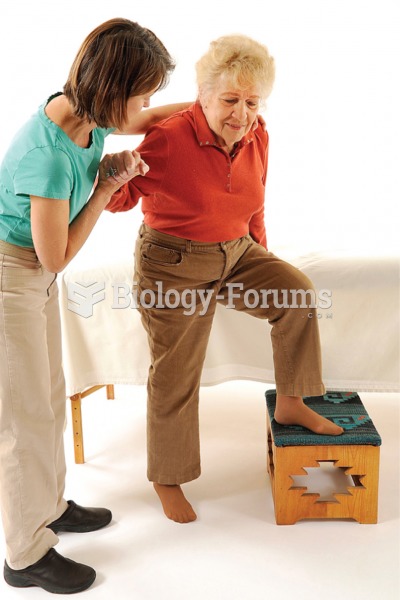
Elderly adults are at greatest risk of stroke and myocardial infarction and have the most to gain from prophylaxis. Patients ages 60 to 80 years with blood pressures above 160/90 mm Hg should benefit from antihypertensive treatment.
The effects of organophosphate poisoning are referred to by using the abbreviations “SLUD” or “SLUDGE,” It stands for: salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, GI upset, and emesis.
Walt Disney helped combat malaria by making an animated film in 1943 called The Winged Scourge. This short film starred the seven dwarfs and taught children that mosquitos transmit malaria, which is a very bad disease. It advocated the killing of mosquitos to stop the disease.