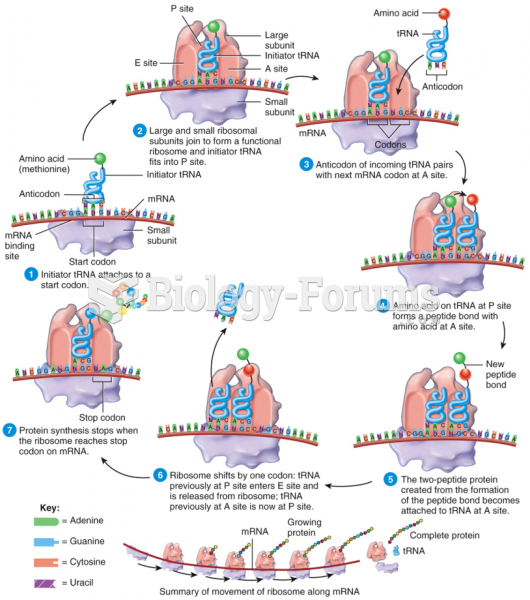
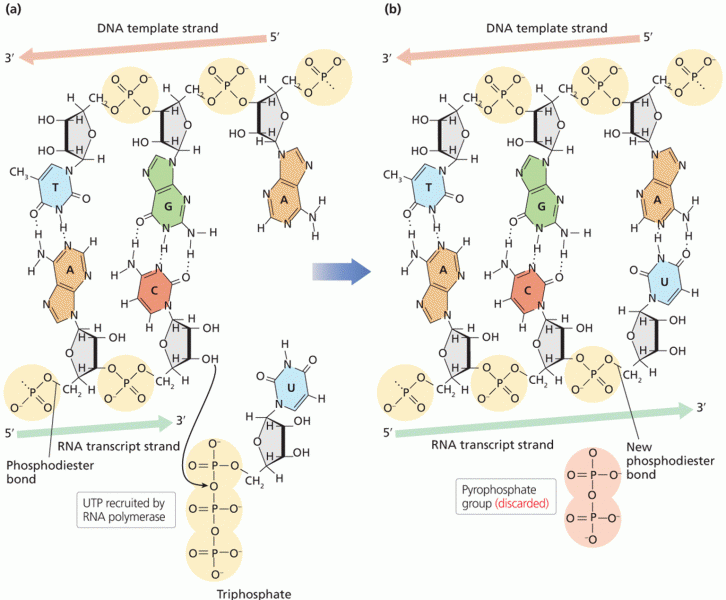
|
|
|
Did you know?
Patients who have undergone chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer often complain of a lack of mental focus; memory loss; and a general diminution in abilities such as multitasking, attention span, and general mental agility.
Did you know?
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
Did you know?
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Did you know?
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.
Did you know?
Despite claims by manufacturers, the supplement known as Ginkgo biloba was shown in a study of more than 3,000 participants to be ineffective in reducing development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people.