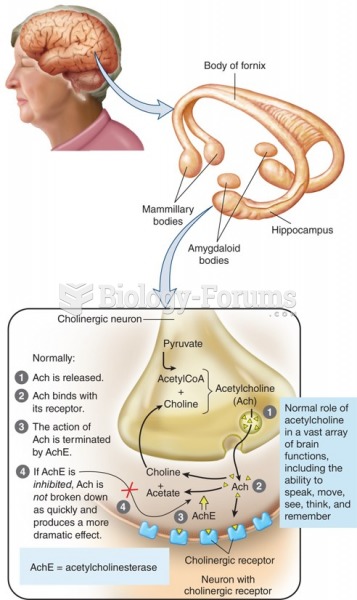
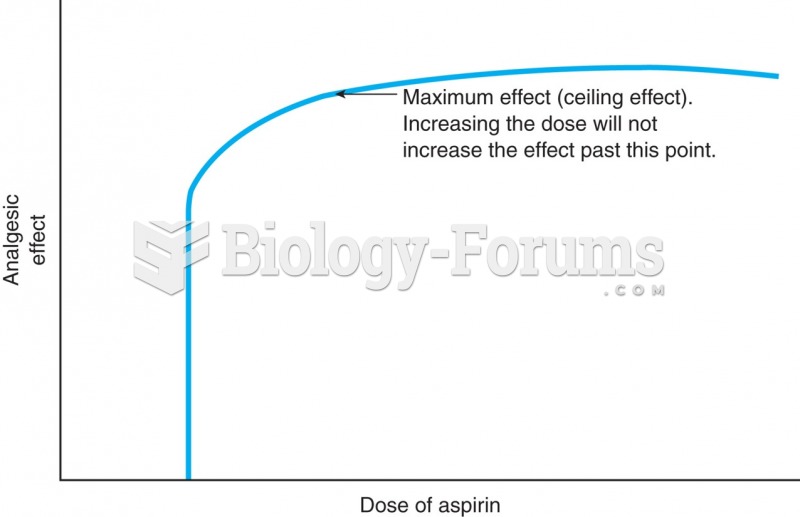
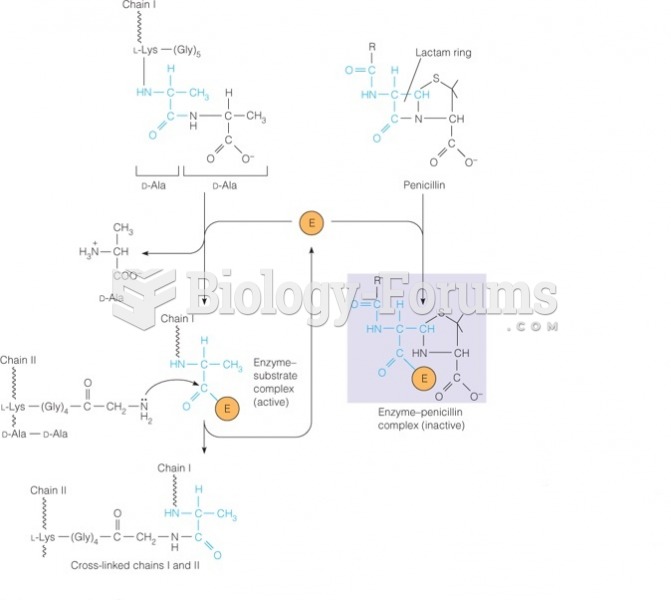
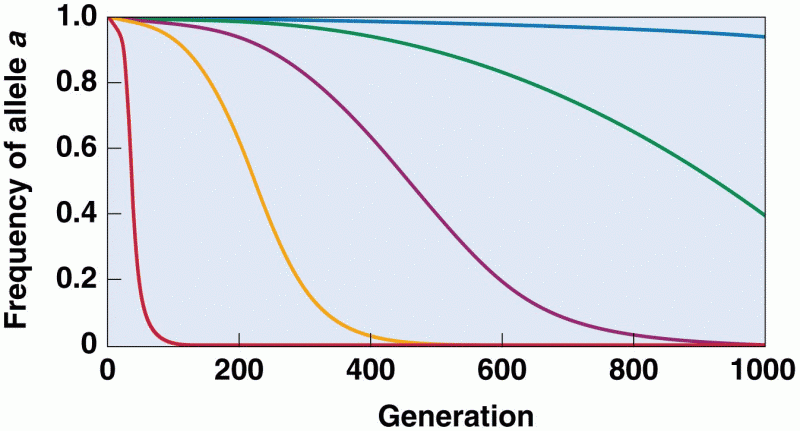
|
|
|
Fewer than 10% of babies are born on their exact due dates, 50% are born within 1 week of the due date, and 90% are born within 2 weeks of the date.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Women are two-thirds more likely than men to develop irritable bowel syndrome. This may be attributable to hormonal changes related to their menstrual cycles.
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.
Disorders that may affect pharmacodynamics include genetic mutations, malnutrition, thyrotoxicosis, myasthenia gravis, Parkinson's disease, and certain forms of insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus.
 Before the advent of vaccinations and antibiotics, infectious diseases such as cholera were the scou
Before the advent of vaccinations and antibiotics, infectious diseases such as cholera were the scou
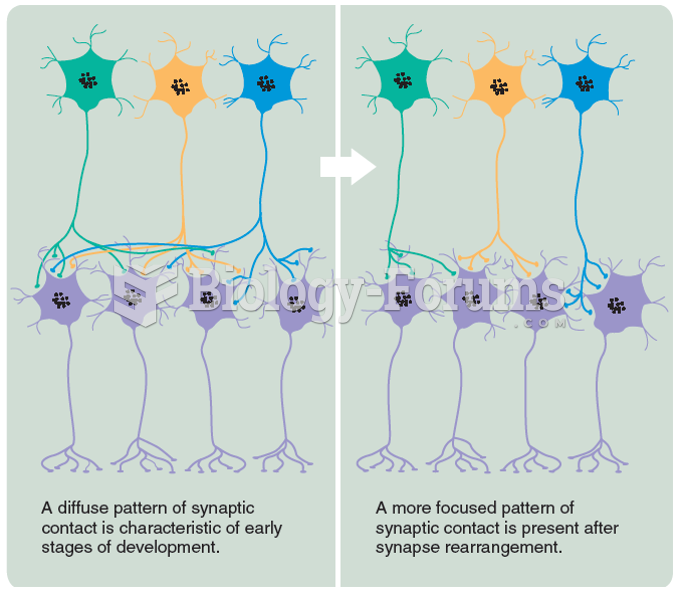 The effect of neuron death and synapse rearrangement on the selectivity of synaptic transmission. ...
The effect of neuron death and synapse rearrangement on the selectivity of synaptic transmission. ...