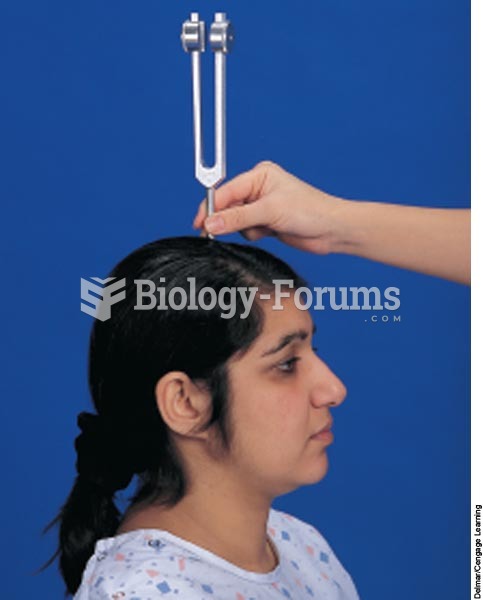
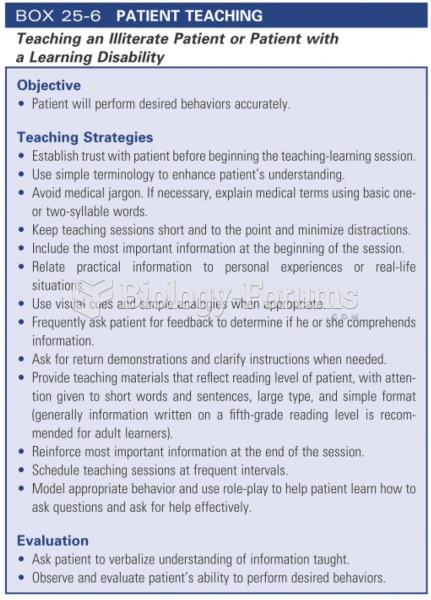
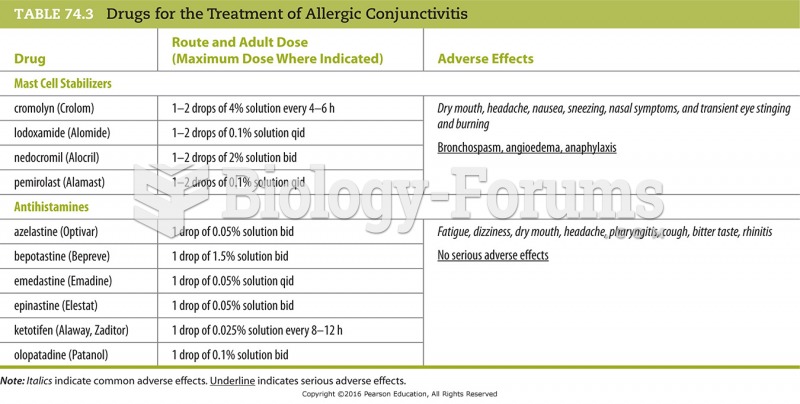
|
|
|
More than 2,500 barbiturates have been synthesized. At the height of their popularity, about 50 were marketed for human use.
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
Lower drug doses for elderly patients should be used first, with titrations of the dose as tolerated to prevent unwanted drug-related pharmacodynamic effects.
About 60% of newborn infants in the United States are jaundiced; that is, they look yellow. Kernicterus is a form of brain damage caused by excessive jaundice. When babies begin to be affected by excessive jaundice and begin to have brain damage, they become excessively lethargic.
Amoebae are the simplest type of protozoans, and are characterized by a feeding and dividing trophozoite stage that moves by temporary extensions called pseudopodia or false feet.