Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1
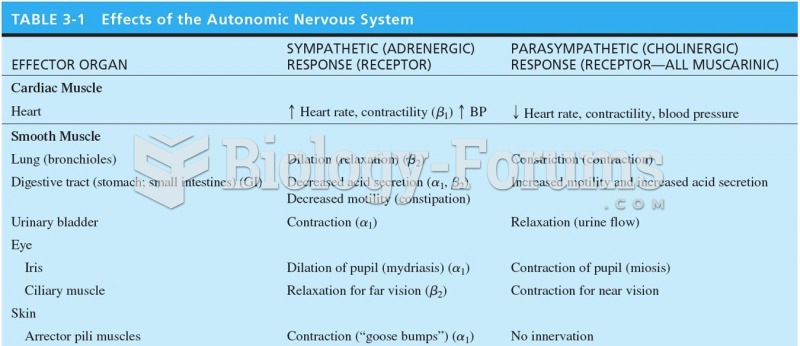
Rationale 1: Abdominal cramping is a common side effect of bethanechol.
Rationale 2: More commonly, bethanechol would cause hypotension.
Rationale 3: Bethanechol might cause diarrhea and abdominal cramping.
Rationale 4: Bethanechol might cause bradycardia.
Global Rationale: Abdominal cramping is a common side effect of bethanechol. Bethanechol would cause hypotension, not hypertension; diarrhea and abdominal cramping not constipation; bradycardia and not tachycardia.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 1,2,5
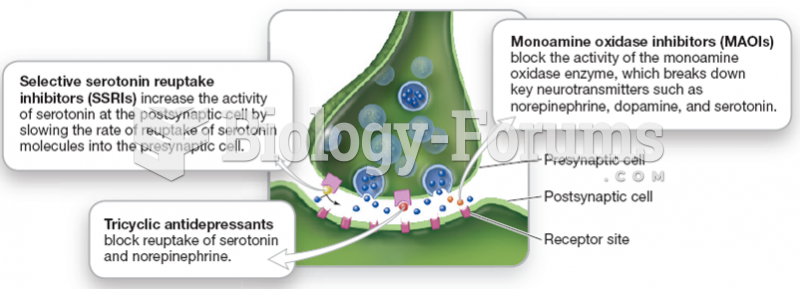
Rationale 1: Cholinergic drugs increase gastric acid secretion and should be used with caution with corticosteroids such as Decadron.
Rationale 2: Cholinergic drugs increase gastric acid secretion and should be used with caution with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen.
Rationale 3: Warfarin administration does not need to be questioned for the client with myasthenia gravis.
Rationale 4: NPH insulin administration does not need to be questioned for the client with myasthenia gravis.
Rationale 5: Drugs that interfere with neuromuscular transmission such as lidocaine should be used with caution in the client with myasthenia gravis because severe muscular weakness may result.
Global Rationale: Cholinergic drugs increase gastric acid secretion and should be used with caution with corticosteroids such as Decadron and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen. Drugs that interfere with neuromuscular transmission such as lidocaine should be used with caution in the client with myasthenia gravis because severe muscular weakness may result. Warfarin administration and NPH insulin administration do not need to be questioned for the client with myasthenia gravis.