|
|
|
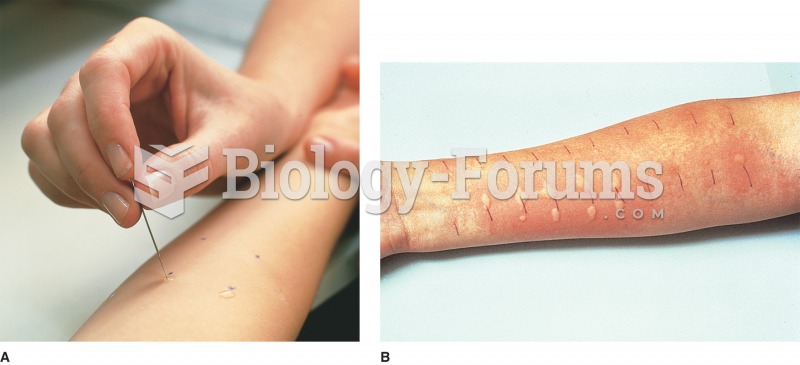
Dogs have been used in studies to detect various cancers in human subjects. They have been trained to sniff breath samples from humans that were collected by having them breathe into special tubes. These people included 55 lung cancer patients, 31 breast cancer patients, and 83 cancer-free patients. The dogs detected 54 of the 55 lung cancer patients as having cancer, detected 28 of the 31 breast cancer patients, and gave only three false-positive results (detecting cancer in people who didn't have it).
Warfarin was developed as a consequence of the study of a strange bleeding disorder that suddenly occurred in cattle on the northern prairies of the United States in the early 1900s.
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
The people with the highest levels of LDL are Mexican American males and non-Hispanic black females.
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
 The tone of the nurse-patient introduction sets the stage for the patient interview and patient care
The tone of the nurse-patient introduction sets the stage for the patient interview and patient care
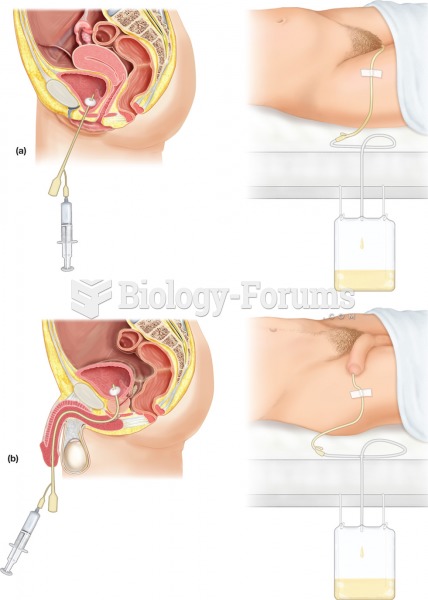 Urinary catheterization. The procedure involves the insertion of a flexible tube, or catheter, throu
Urinary catheterization. The procedure involves the insertion of a flexible tube, or catheter, throu