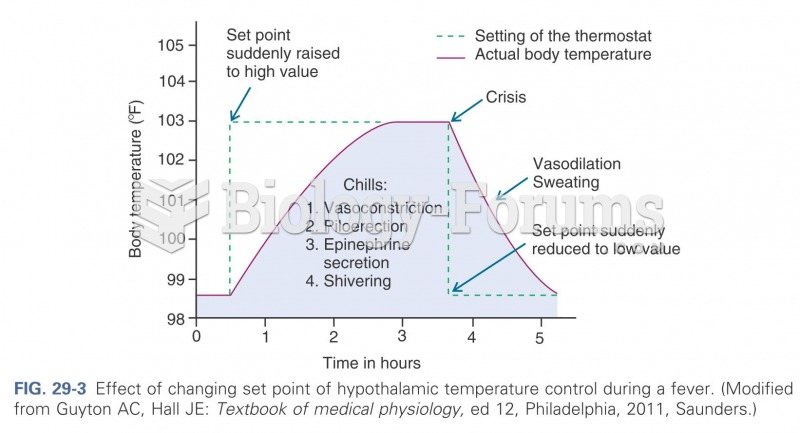
|
|
|
Pregnant women usually experience a heightened sense of smell beginning late in the first trimester. Some experts call this the body's way of protecting a pregnant woman from foods that are unsafe for the fetus.
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
The liver is the only organ that has the ability to regenerate itself after certain types of damage. As much as 25% of the liver can be removed, and it will still regenerate back to its original shape and size. However, the liver cannot regenerate after severe damage caused by alcohol.
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
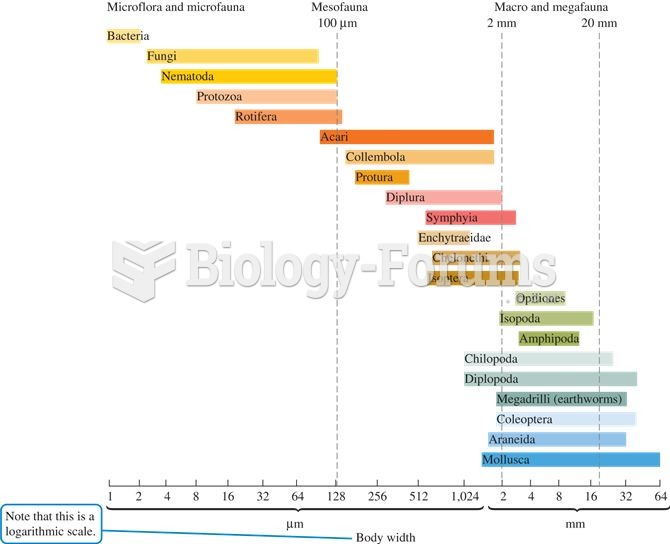 Detritivores are often classified according to their body size as microflora, microfauna, mesofauna,
Detritivores are often classified according to their body size as microflora, microfauna, mesofauna,
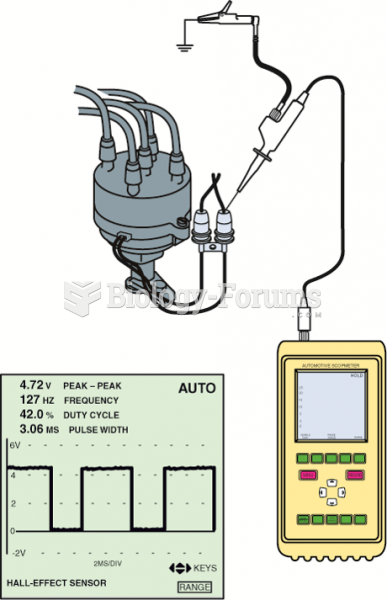
 A Hall-effect sensor produces a digital on-off voltage signal whether it is used with a blade or a ...
A Hall-effect sensor produces a digital on-off voltage signal whether it is used with a blade or a ...