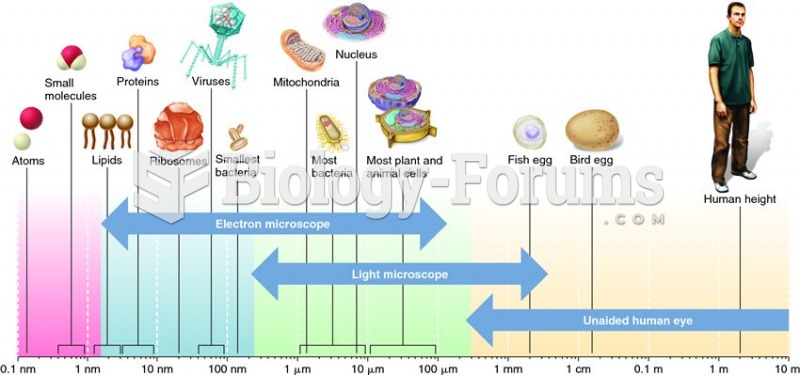
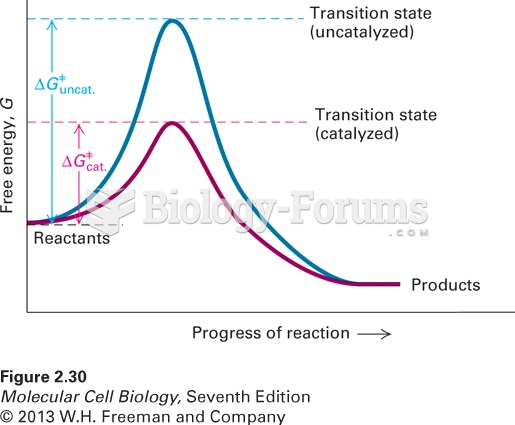
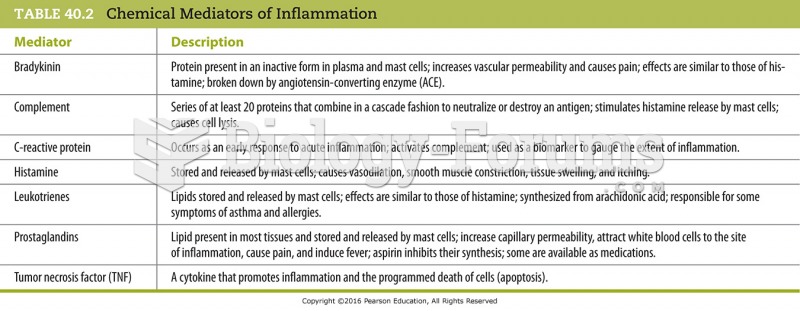
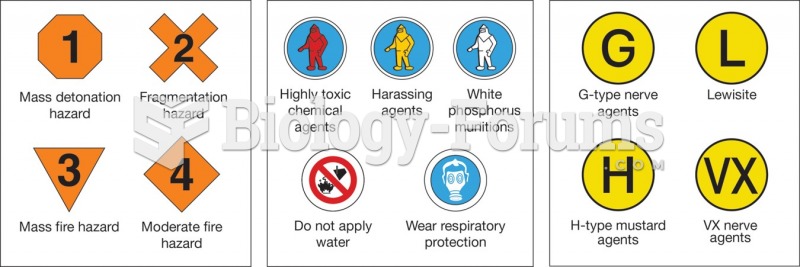
Answer to Question 1
The chemicals that frequently cause chemical burn injuries include acids and alkalies; soaps, detergents, and cleaning compounds; solvents and degreasers; calcium hydroxide (a chemical used in cement and plaster); potassium hydroxide (an ingredient in drain cleaners and other cleaning solutions); and sulfuric acid (battery acid). Almost 46 percent of all chemical burn injuries occur while workers are cleaning equipment, tools, and vehicles.
Answer to Question 2
Motor vehicle accidents. Motor vehicle accidents are the leading cause of accidental deaths in the United States every year. They include deaths resulting from accidents involving mechanically or electrically powered vehicles (excluding rail vehicles) that occur on or off the road. In a typical year, there are approximately 47,000 such deaths in the United States.
Falls. This category includes all deaths from falls except those associated with transport vehicles. For example, a person who is killed as the result of falling while boarding a bus or train would not be included in this category. In a typical year, there are approximately 13,000 deaths in the United States from falls.
Poisoning. The poisoning category is divided into two subcategories: (1) poisoning by solids and liquids, and (2) poisoning by gases and vapors. The first category includes deaths that result from the ingestion of drugs, medicine, widely recognized solid and liquid poisons, mushrooms and shellfish. It does not include poisoning from spoiled food or salmonella. The second category includes deaths caused by incomplete combustion (for example, gas vapors from an oven or unlit pilot light) or from carbon monoxide (for example, exhaust fumes from an automobile). In a typical year, there are approximately 6,000 deaths in the first category and 1,000 in the second.
Drowning. This category includes work-related and nonwork-related drownings, but excludes those associated with floods or other natural disasters. In a typical year, there are approximately 5,000 deaths from drowning in the United States.
Fire-related injuries. This category includes deaths from burns, asphyxiation, falls, and those that result from falling objects in a fire. In a typical year, there are more than 4,000 fire-related deaths in the United States.
Suffocation (ingested object). This category includes deaths from the ingestion of an object that blocks the air passages. In many such deaths, the ingested object is food. In a typical year, there are approximately 4,000 such suffocation deaths in the United States.
Firearms. This category includes deaths that result when recreational activities involving firearms or household accidents involving firearms result in death. For example, a person killed in the home while cleaning a firearm would be included in this category. However, a person killed in combat would not be. In a typical year, there are approximately 2,000 deaths in this category.
Others. This category includes deaths resulting from medical complications arising out of mistakes made by health care professionals, air transport injuries, interaction with machinery, mechanical suffocation, and the impact of falling objects. In a typical year, there more than 14,000 deaths in these subcategories.