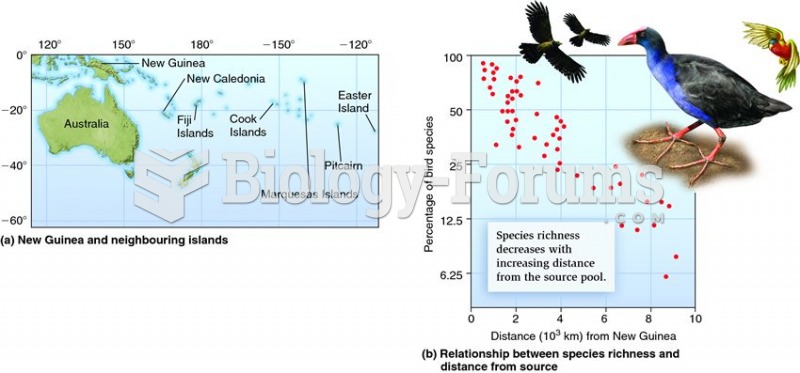
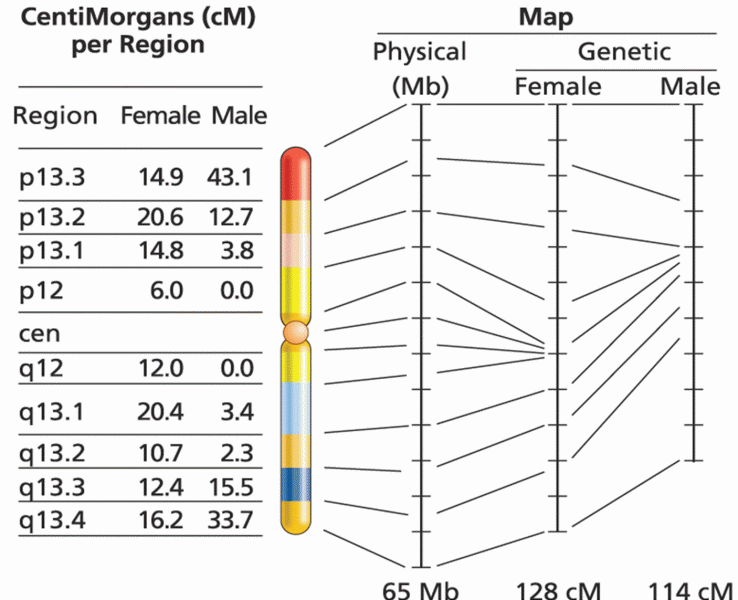
|
|
|
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
Atropine, along with scopolamine and hyoscyamine, is found in the Datura stramonium plant, which gives hallucinogenic effects and is also known as locoweed.
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).
Certain rare plants containing cyanide include apricot pits and a type of potato called cassava. Fortunately, only chronic or massive ingestion of any of these plants can lead to serious poisoning.
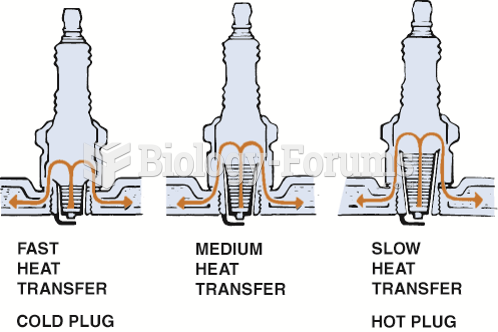 The heat range of a spark plug is determined by the distance the heat has to flow from the tip to ...
The heat range of a spark plug is determined by the distance the heat has to flow from the tip to ...
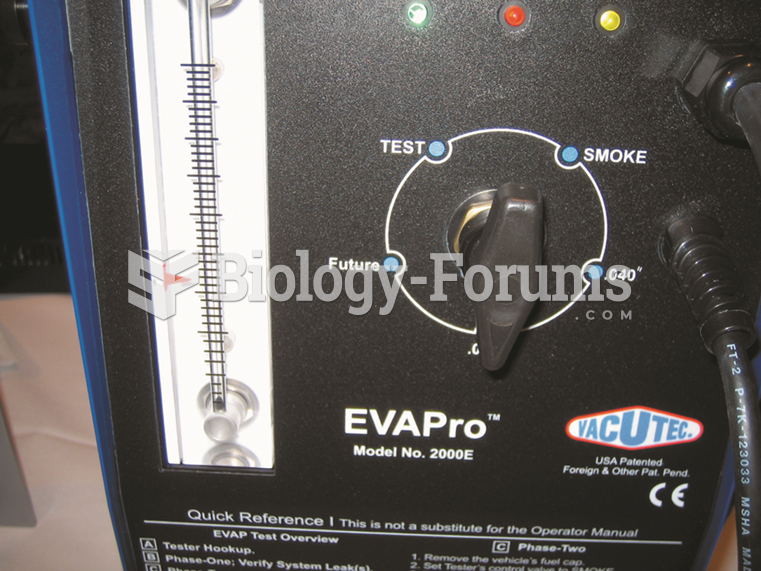 To test for a leak, this tester was set to the 0.020 inch hole and turned on. The ball rose in the ...
To test for a leak, this tester was set to the 0.020 inch hole and turned on. The ball rose in the ...