This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
Did you know?
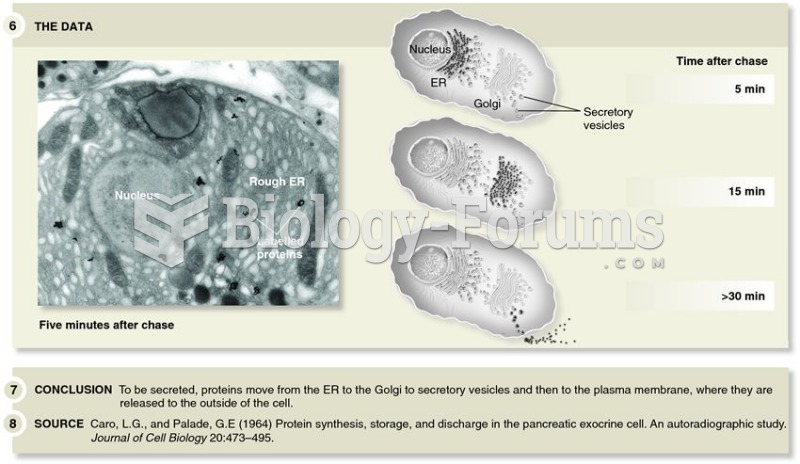
Amoebae are the simplest type of protozoans, and are characterized by a feeding and dividing trophozoite stage that moves by temporary extensions called pseudopodia or false feet.
Did you know?
The oldest recorded age was 122. Madame Jeanne Calment was born in France in 1875 and died in 1997. She was a vegetarian and loved olive oil, port wine, and chocolate.
Did you know?
Sperm cells are so tiny that 400 to 500 million (400,000,000–500,000,000) of them fit onto 1 tsp.
Did you know?
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.