|
|
|
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
In 2012, nearly 24 milliion Americans, aged 12 and older, had abused an illicit drug, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
Pink eye is a term that refers to conjunctivitis, which is inflammation of the thin, clear membrane (conjunctiva) over the white part of the eye (sclera). It may be triggered by a virus, bacteria, or foreign body in the eye. Antibiotic eye drops alleviate bacterial conjunctivitis, and antihistamine allergy pills or eye drops help control allergic conjunctivitis symptoms.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
 (a) Feeding by bear on salmon results in large allochthonous inputs of nutrients into (b) the forest
(a) Feeding by bear on salmon results in large allochthonous inputs of nutrients into (b) the forest
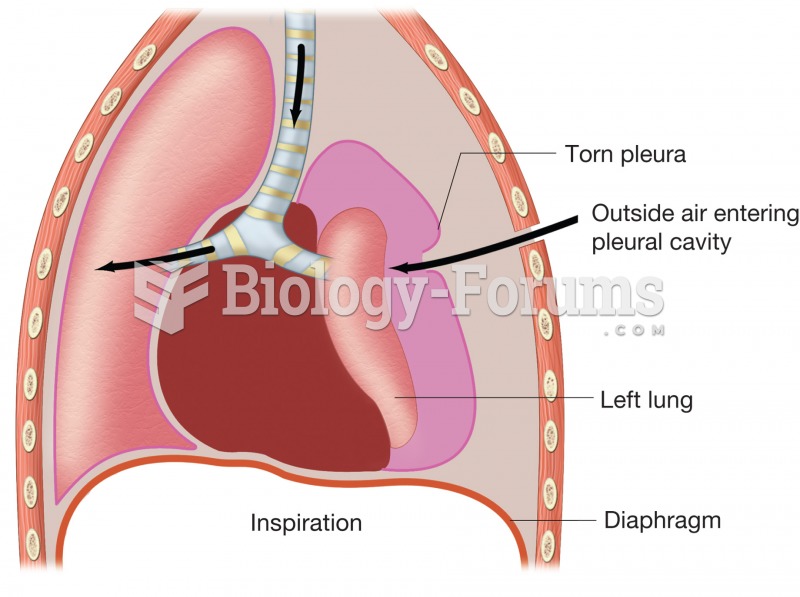 Pneumothorax. Figure illustrates how puncture of thoracic wall and tearing of pleural membrane allow
Pneumothorax. Figure illustrates how puncture of thoracic wall and tearing of pleural membrane allow