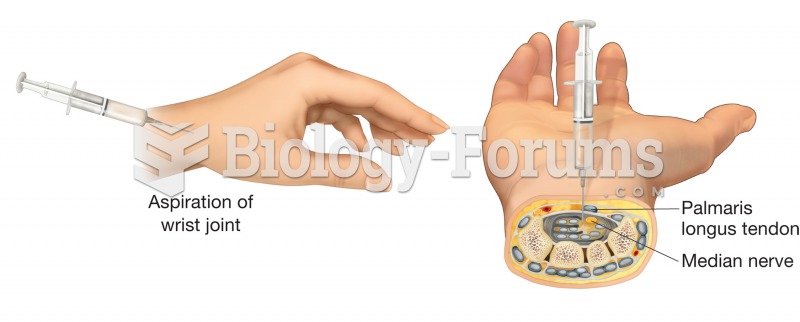
|
|
|
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) was originally known as the Communicable Disease Center, which was formed to fight malaria. It was originally headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, since the Southern states faced the worst threat from malaria.
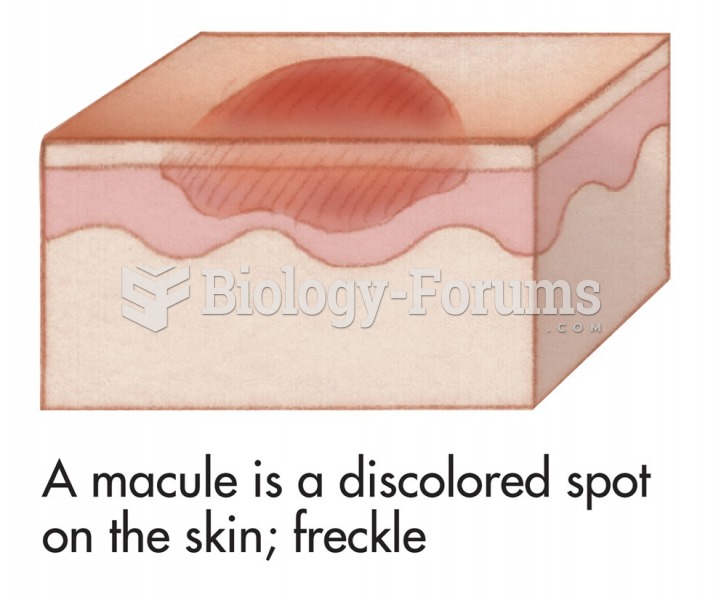
Liver spots have nothing whatsoever to do with the liver. They are a type of freckles commonly seen in older adults who have been out in the sun without sufficient sunscreen.
One way to reduce acid reflux is to lose two or three pounds. Most people lose weight in the belly area first when they increase exercise, meaning that heartburn can be reduced quickly by this method.
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.