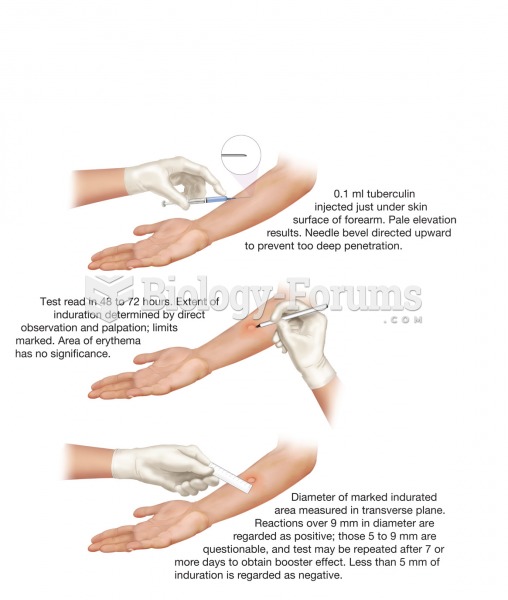
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
More than 2,500 barbiturates have been synthesized. At the height of their popularity, about 50 were marketed for human use.
Did you know?
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
Did you know?
The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 and occurred in Boston. A kidney from an identical twin was transplanted into his dying brother's body and was not rejected because it did not appear foreign to his body.
Did you know?
The oldest recorded age was 122. Madame Jeanne Calment was born in France in 1875 and died in 1997. She was a vegetarian and loved olive oil, port wine, and chocolate.
Did you know?
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.