|
|
|
Did you know?
Vaccines prevent between 2.5 and 4 million deaths every year.
Did you know?
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
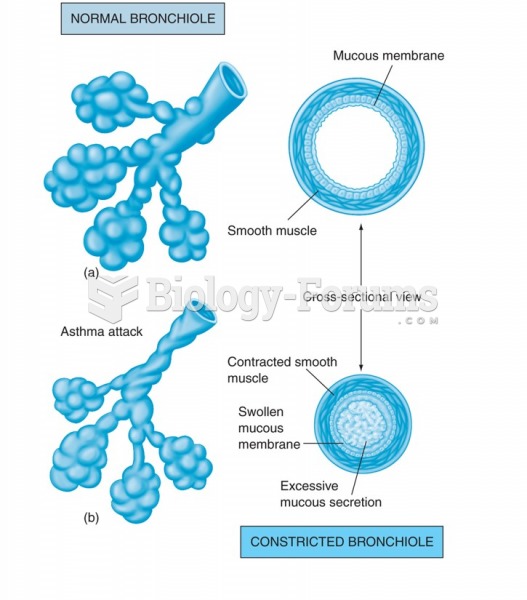
Did you know?
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Did you know?
Cyanide works by making the human body unable to use oxygen.
Did you know?
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.