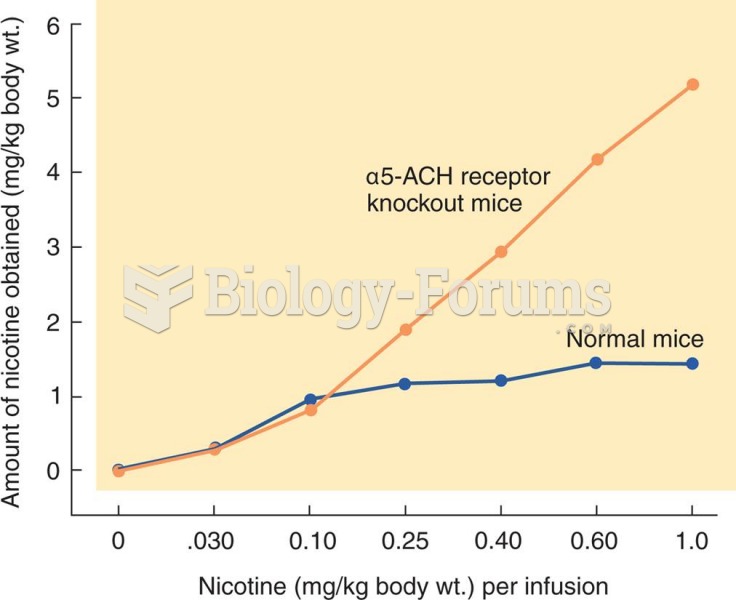
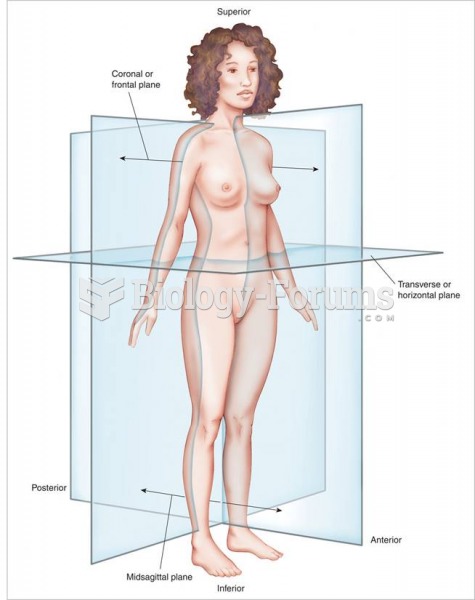
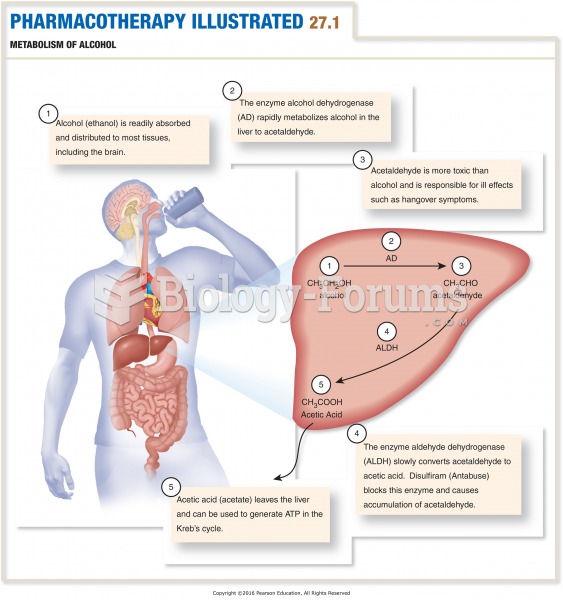
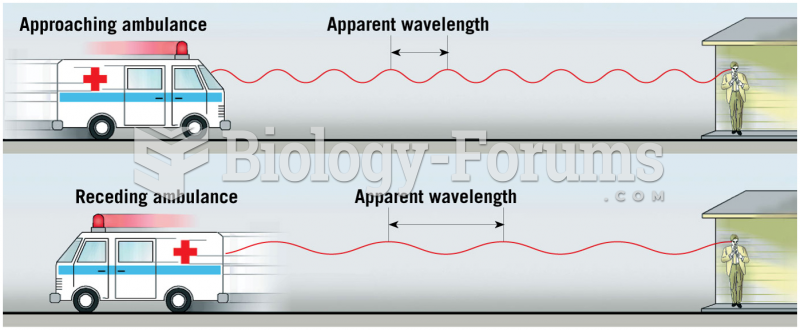
|
|
|
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.
It is widely believed that giving a daily oral dose of aspirin to heart attack patients improves their chances of survival because the aspirin blocks the formation of new blood clots.
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).