|
|
|
Recent studies have shown that the number of medication errors increases in relation to the number of orders that are verified per pharmacist, per work shift.
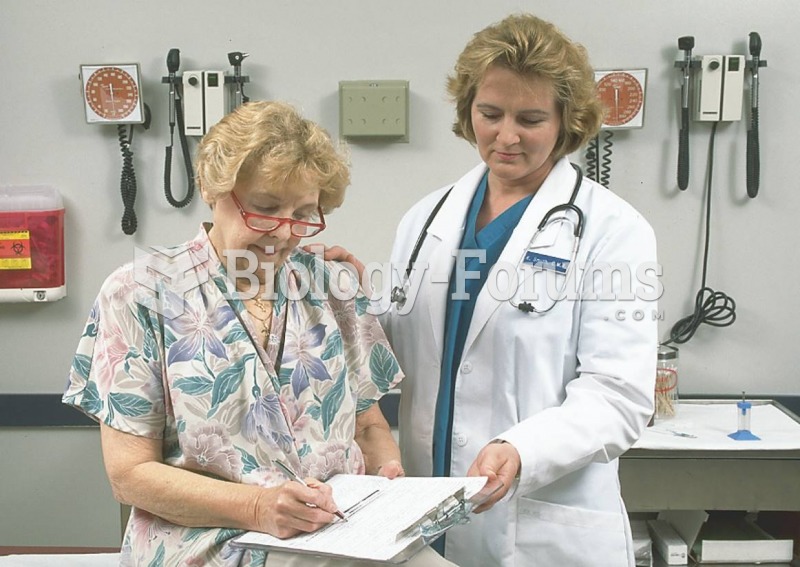
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."
Amoebae are the simplest type of protozoans, and are characterized by a feeding and dividing trophozoite stage that moves by temporary extensions called pseudopodia or false feet.