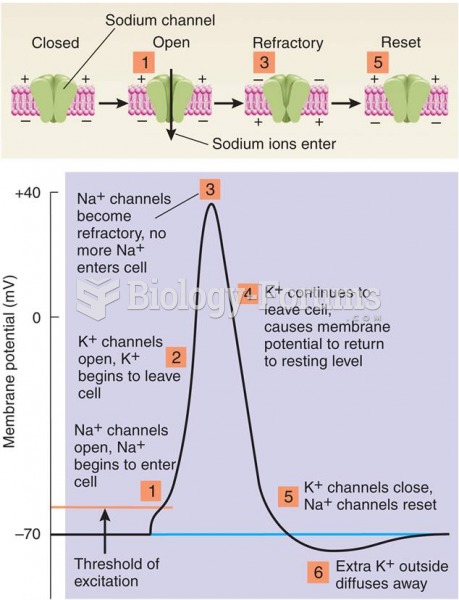
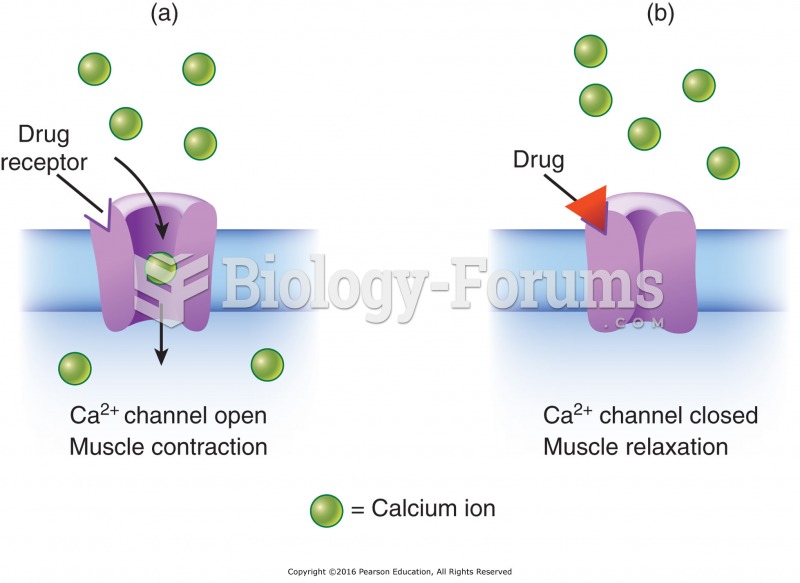
Answer to Question 1
The availability of vitamin C supplements and the publication of books recommending vitamin C to prevent colds and cancer have led many people to take large doses of vitamin C. Not surprisingly, side effects of vitamin C supplementation such as gastrointestinal distress and diarrhea have been reported. The UL for vitamin C was established based on these symptoms.
Several instances of interference with medical regimens are also known. Large amounts of vitamin C excreted in the urine obscure the results of tests used to detect glucose or ketones in the diagnosis of diabetes. In some instances, excess vitamin C gives a false positive result; in others, a false negative. People taking anticlotting medications may unwittingly counteract the effect if they also take massive doses of vitamin C. Those with kidney disease, a tendency toward gout, or a genetic abnormality that alters vitamin C's breakdown to its excretion products are prone to forming kidney stones if they take large doses of vitamin C. Vitamin C supplements may adversely affect people with iron overload. Vitamin C enhances iron absorption and releases iron from body stores; too much free iron causes the kind of cellular damage typical of free radicals. These adverse consequences illustrate how vitamin C can act as a prooxidant when quantities exceed the body's needs.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Overt Deficiencies
In the United States, adults rarely suffer nutrient deficiency diseases such as scurvy, pellagra, and beriberi, but nutrient deficiencies do still occur. To correct an overt deficiency disease, a physician may prescribe therapeutic doses two to ten times the RDA (or AI) of a nutrient. At such high doses, the supplement is having a pharmacological effect and acting as a drug.
Support Increased Nutrient Needs
Nutrient needs increase during certain stages of life, making it difficult to meet some of those needs without supplementation. For example, women who lose a lot of blood and therefore a lot of iron during menstruation each month may need an iron supplement. Women of childbearing age need folate supplements to reduce the risks of neural tube defects. Similarly, pregnant women and women who are breastfeeding their infants have exceptionally high nutrient needs and so usually need special supplements. Newborns routinely receive a single dose of vitamin K at birth to prevent abnormal bleeding. Infants may need other supplements as well, depending on whether they are breastfed or receiving formula, and on whether the water they drink contains fluoride.
Improve Nutrition Status
In contrast to the classical deficiencies, which present a multitude of symptoms and are relatively easy to recognize, subclinical deficiencies are subtle and easy to overlookand they are also more likely to occur. Without fortification or supplementation, many adults in the United States fall short of recommended intakes for several vitamins and minerals. People who do not eat enough food to deliver the needed amounts of nutrients, such as habitual dieters and the elderly, risk developing subclinical deficiencies. Similarly, vegetarians who restrict their use of entire food groups without appropriate substitutions may fail to fully meet their nutrient needs. If there is no way for these people to eat enough nutritious foods to meet their needs, then vitamin-mineral supplements may be appropriate to help prevent nutrient deficiencies.
Improve the Body's Defenses
Health-care professionals may provide special supplementation to people being treated for addictions to alcohol or other drugs and to people with prolonged illnesses, extensive injuries, or other severe stresses such as surgery. Illnesses that interfere with appetite, eating, or nutrient absorption impair nutrition status. For example, the stomach condition atrophic gastritis often creates a vitamin B12 deficiency. In addition, nutrient needs are often heightened by diseases or medications. In all these cases, supplements are appropriate.
Reduce Disease Risks
Few people consume the optimal amounts of all the vitamins and minerals by diet alone. Inadequate intakes have been linked to chronic diseases such as heart disease, some cancers, and osteoporosis. For this reason, some physicians recommend that all adults take vitamin- mineral supplements. Such regular supplementation would provide an optimum intake to enhance metabolic harmony and prevent disease at relatively little cost. Others recognize the lack of conclusive evidence and the potential harm of supplementation and advise against such a recommendation. A statement from the National Institutes of Health acknowledges that evidence is insufficient to recommend either for or against the use of supplements to prevent chronic diseases.