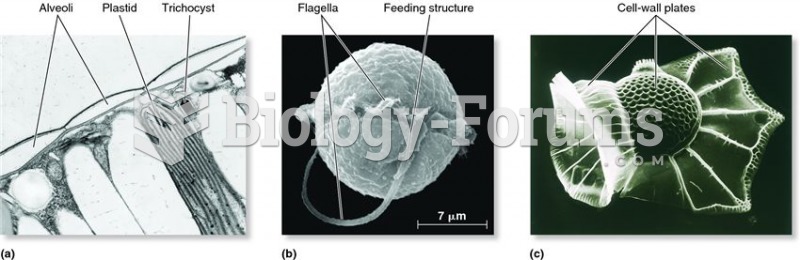
|
|
|
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
About 60% of newborn infants in the United States are jaundiced; that is, they look yellow. Kernicterus is a form of brain damage caused by excessive jaundice. When babies begin to be affected by excessive jaundice and begin to have brain damage, they become excessively lethargic.
 The visual field as seen by a person with (a) glaucoma, (b) macular degeneration, and (c) cataracts.
The visual field as seen by a person with (a) glaucoma, (b) macular degeneration, and (c) cataracts.
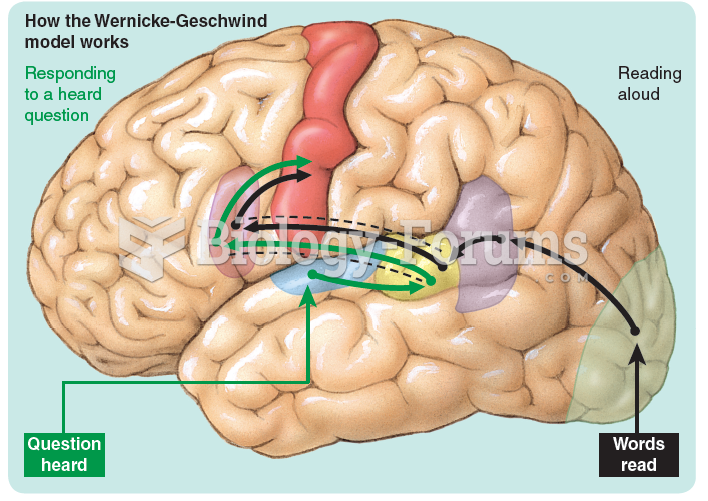 How the Wernicke-Geschwind model works in a person who is responding to a heard question and reading ...
How the Wernicke-Geschwind model works in a person who is responding to a heard question and reading ...