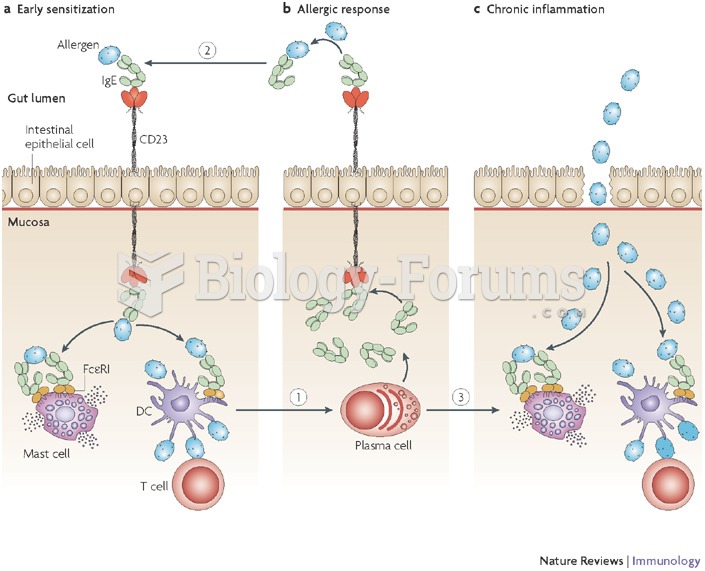
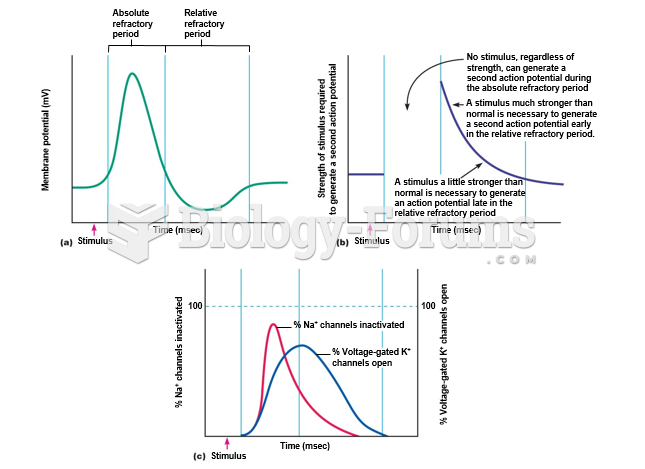
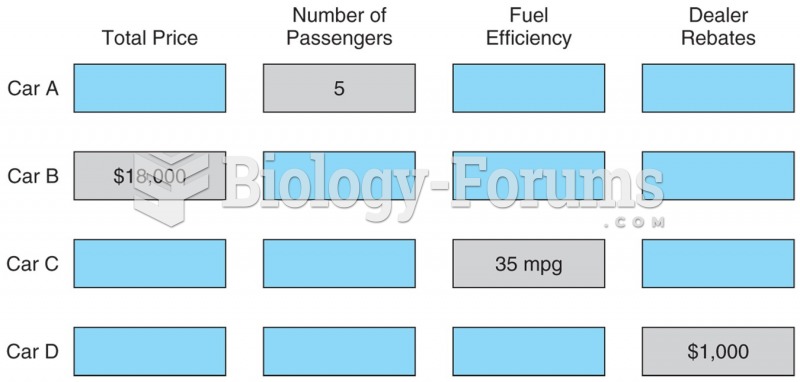
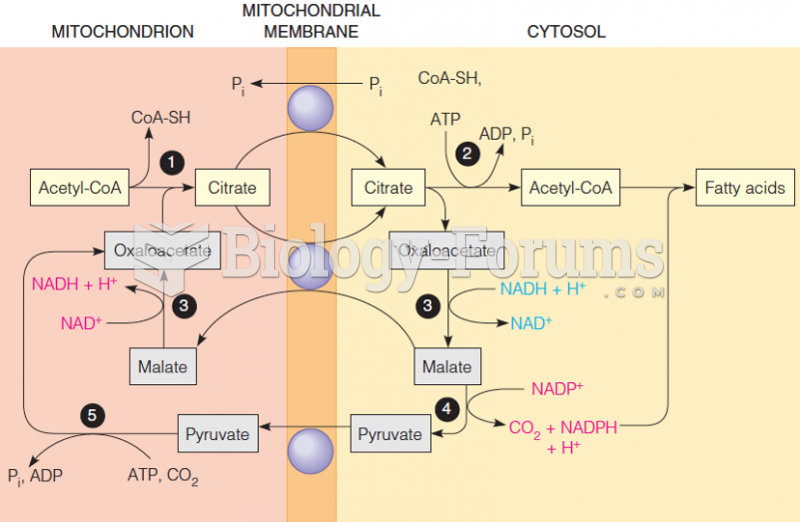
|
|
|
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
Addicts to opiates often avoid treatment because they are afraid of withdrawal. Though unpleasant, with proper management, withdrawal is rarely fatal and passes relatively quickly.
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates’s recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
In 2006, a generic antinausea drug named ondansetron was approved. It is used to stop nausea and vomiting associated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Complications of influenza include: bacterial pneumonia, ear and sinus infections, dehydration, and worsening of chronic conditions such as asthma, congestive heart failure, or diabetes.