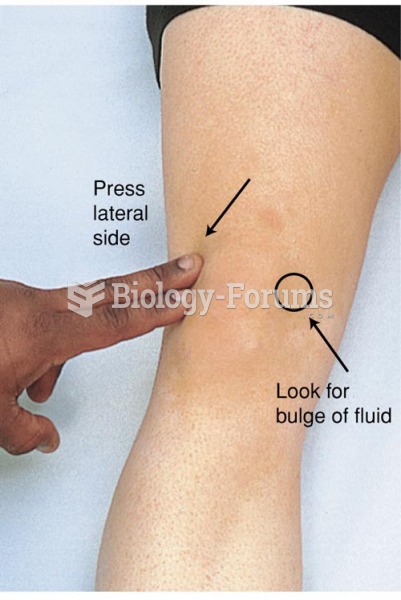
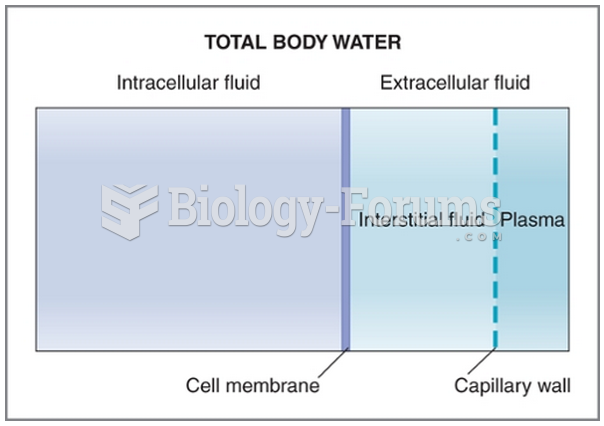
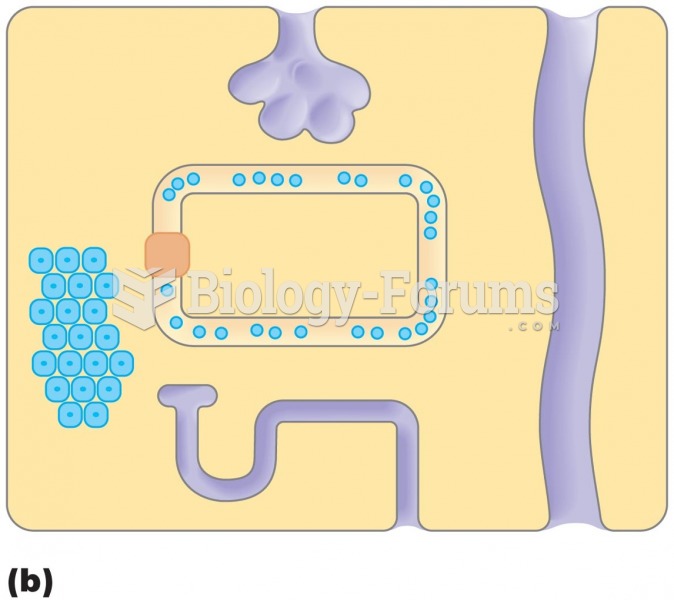
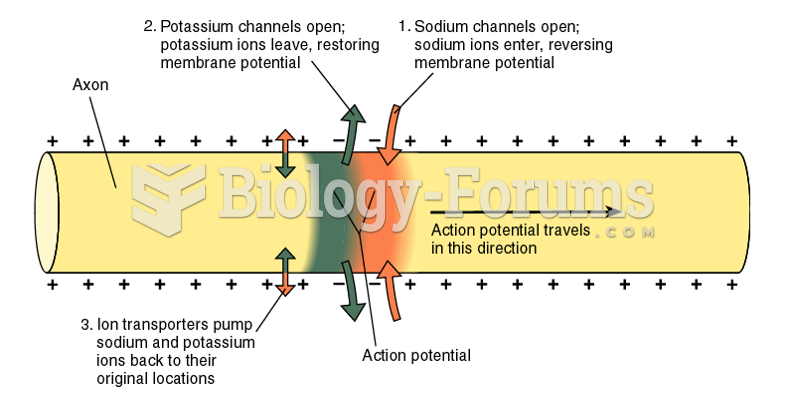
|
|
|
The first oral chemotherapy drug for colon cancer was approved by FDA in 2001.
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
If you use artificial sweeteners, such as cyclamates, your eyes may be more sensitive to light. Other factors that will make your eyes more sensitive to light include use of antibiotics, oral contraceptives, hypertension medications, diuretics, and antidiabetic medications.
Historic treatments for rheumatoid arthritis have included gold salts, acupuncture, a diet consisting of apples or rhubarb, nutmeg, nettles, bee venom, bracelets made of copper, prayer, rest, tooth extractions, fasting, honey, vitamins, insulin, snow collected on Christmas, magnets, and electric convulsion therapy.