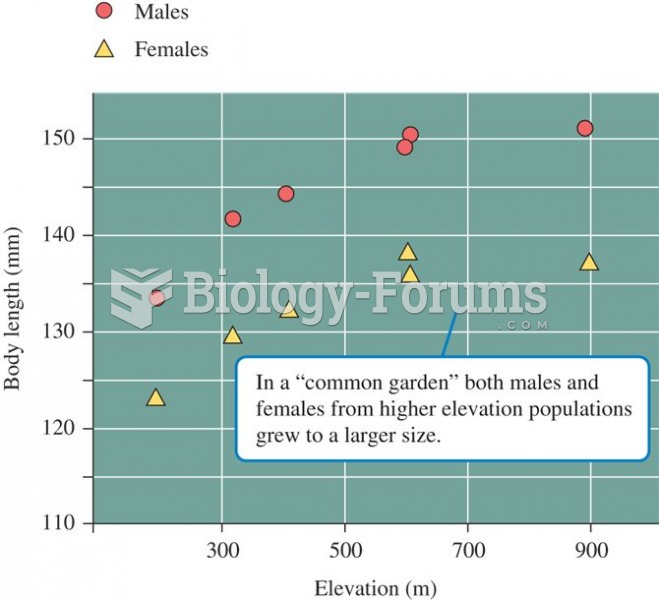
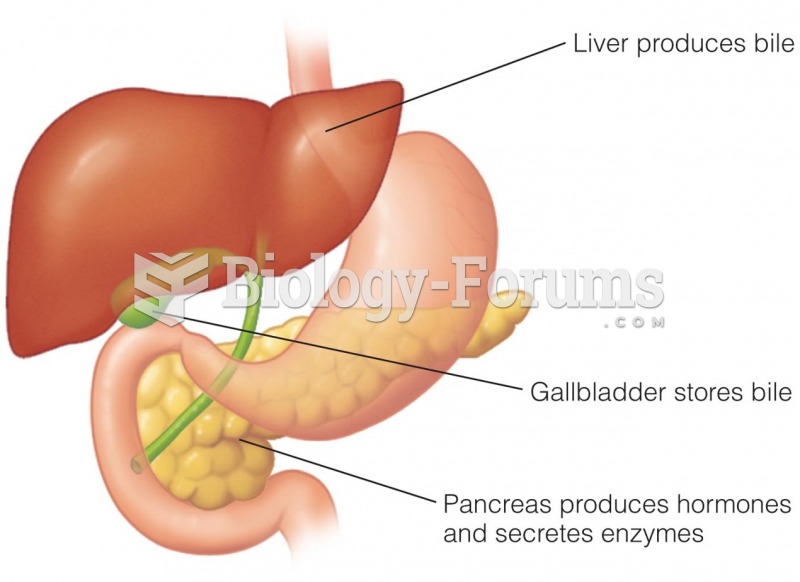
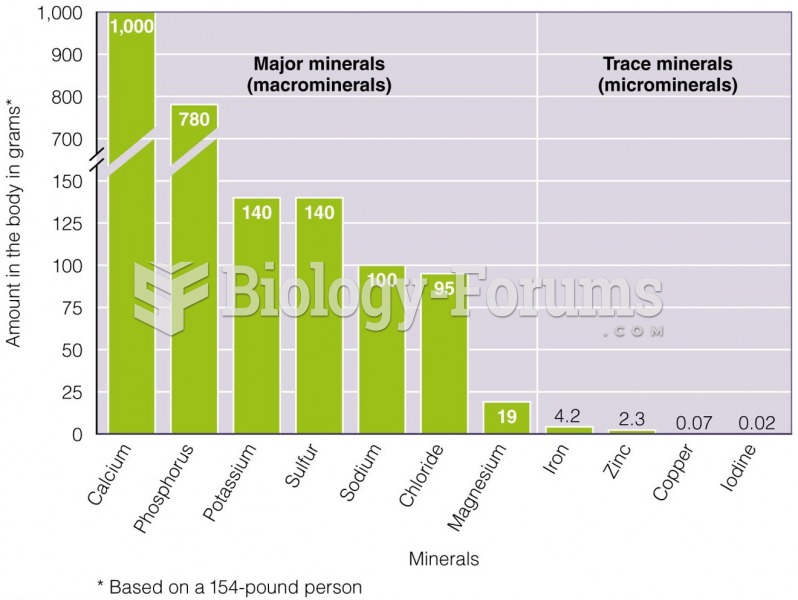
|
|
|
More than 2,500 barbiturates have been synthesized. At the height of their popularity, about 50 were marketed for human use.
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
More than 50% of American adults have oral herpes, which is commonly known as "cold sores" or "fever blisters." The herpes virus can be active on the skin surface without showing any signs or causing any symptoms.
Everyone has one nostril that is larger than the other.
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.