This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
Did you know?
It is important to read food labels and choose foods with low cholesterol and saturated trans fat. You should limit saturated fat to no higher than 6% of daily calories.
Did you know?
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
Did you know?
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
Did you know?
Congestive heart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.
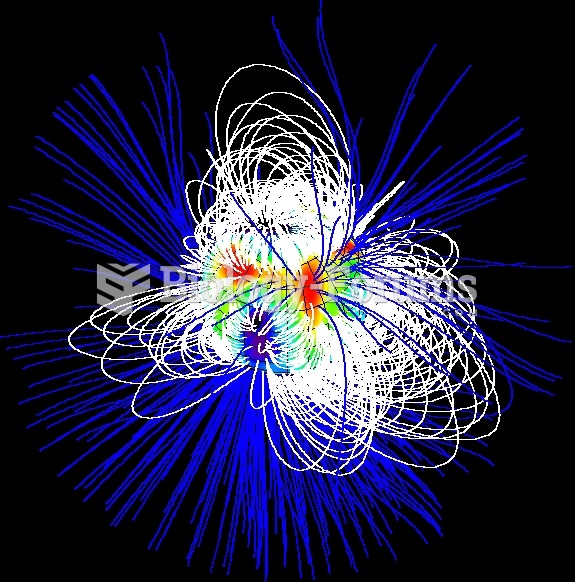 Surface magnetic field of SU Aur (a young star of T Tauri type), reconstructed by means of Zeeman-Do
Surface magnetic field of SU Aur (a young star of T Tauri type), reconstructed by means of Zeeman-Do
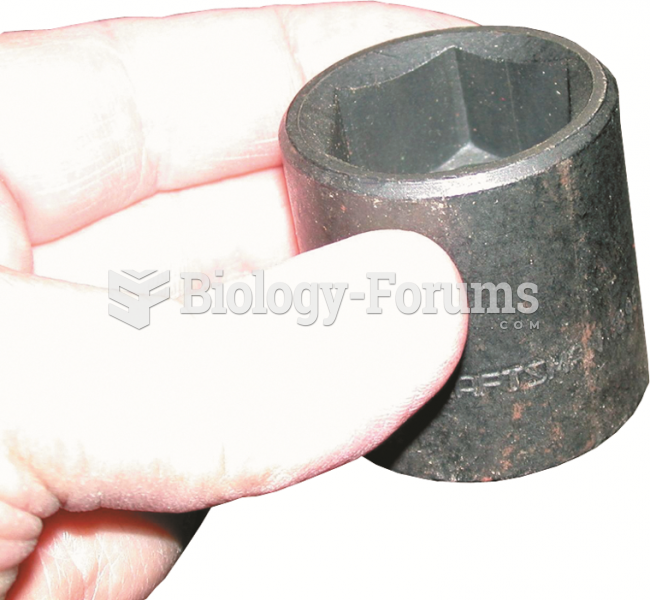 A black impact socket. Always use an impact-type socket whenever using an impact wrench to avoid ...
A black impact socket. Always use an impact-type socket whenever using an impact wrench to avoid ...