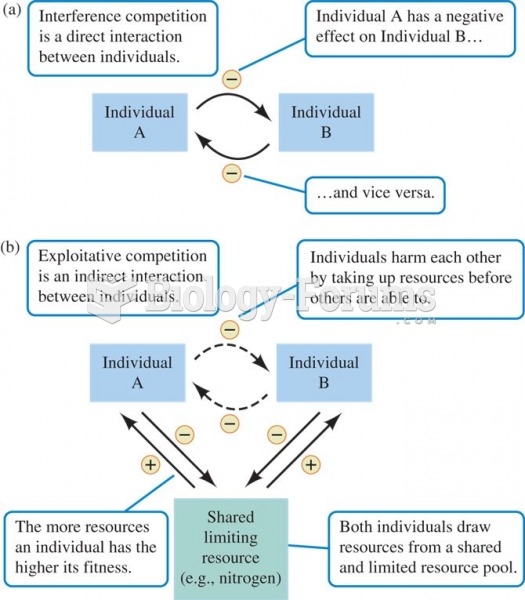
Answer to Question 1
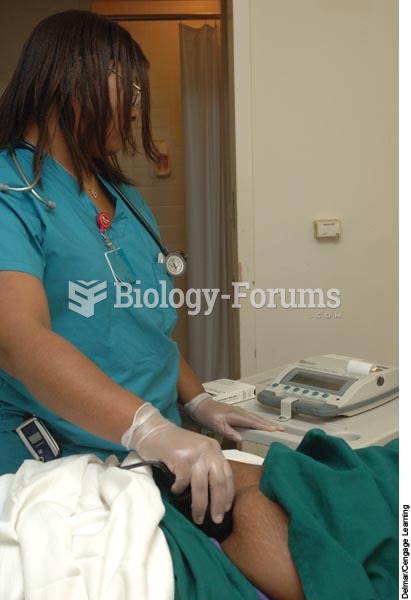
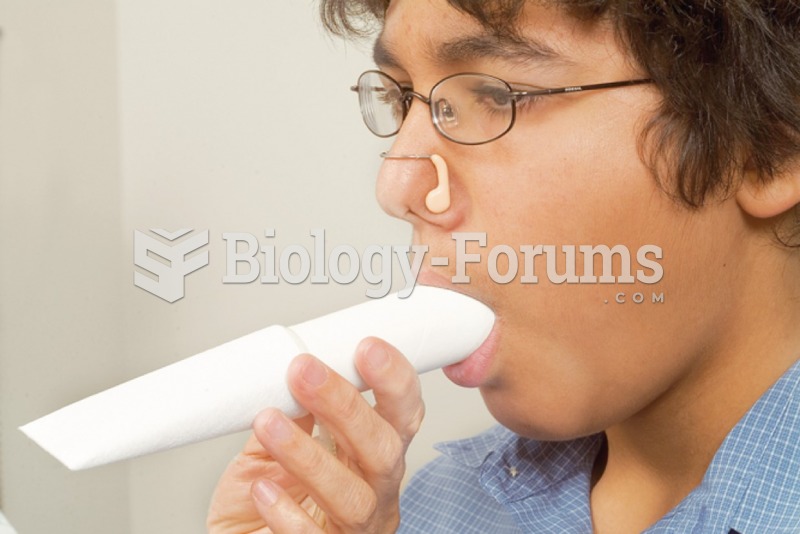
Indirect calorimetry is the most accurate method of measuring resting energy expenditure/resting metabolic rate (other than direct calorimetry, which is not applicable to many settings including the clinical setting). It is based on the fact that energy expenditure is proportional to the body's oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production. Indirect calorimetry is performed by using a metabolic cart at bedside that measures the amount of oxygen consumed and carbon dioxide expelled by the patient (VO2 and VCO2). Using these values, in addition to the patient's basic anthropometric measurements, allow for more accurate energy requirements to be calculated.
Answer to Question 2
Prebiotics: food sources that contain substances that stimulate the beneficial flora of the large intestine. In other words, prebiotics are the food for the beneficial bacteria in the colon.
Examples: oligosaccharides, inulin
Probiotics: microorganism-containing products that are manufactured and sold as food products and supplements. These foods contain actual live microorganisms that have proved to be beneficial for the gut flora. They help improve the microbial balance, which potentially is off balance in IBS patients.
Currently, research supports the use of prebiotics and probiotics in IBS patients to help establish a population of beneficial microbial flora to help with fermentation. However, the ideal dosage or amount has not been determined through research because it is a newer therapy for IBS patients. These are not considered to be a primary treatment option or standard of care, but considering their general safety, supplementing the diet with probiotics may be considered.
Examples of recommended sources include: Yogurt, kefir, cheeses
Suggesting Mrs. Clarke to continue consuming her yogurt if she enjoys it is appropriate. 3/4 cup of Greek yogurt can provide up to 1 billion bacterial colonies.
If the patient does not like foods that contain probiotic cultures, a dietary supplement like Culturelle or Align may be suggested.