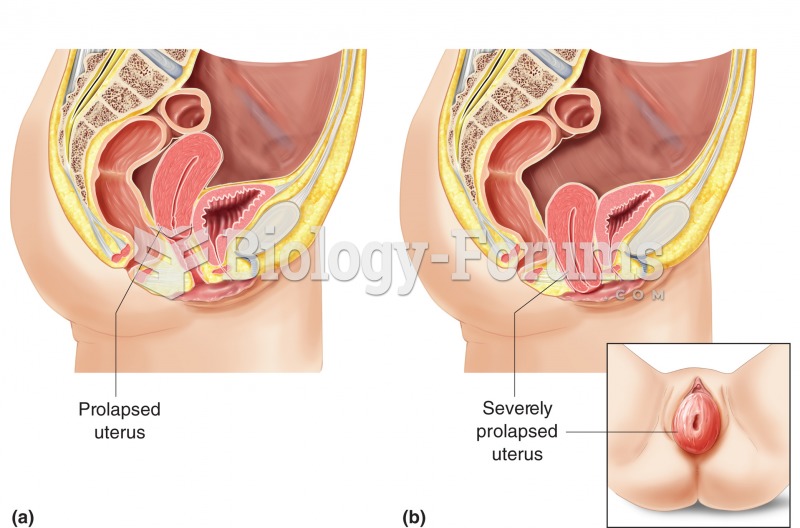
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Medications that are definitely not safe to take when breastfeeding include radioactive drugs, antimetabolites, some cancer (chemotherapy) agents, bromocriptine, ergotamine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.
Did you know?
Increased intake of vitamin D has been shown to reduce fractures up to 25% in older people.
Did you know?
The human body produces and destroys 15 million blood cells every second.
Did you know?
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
Did you know?
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.