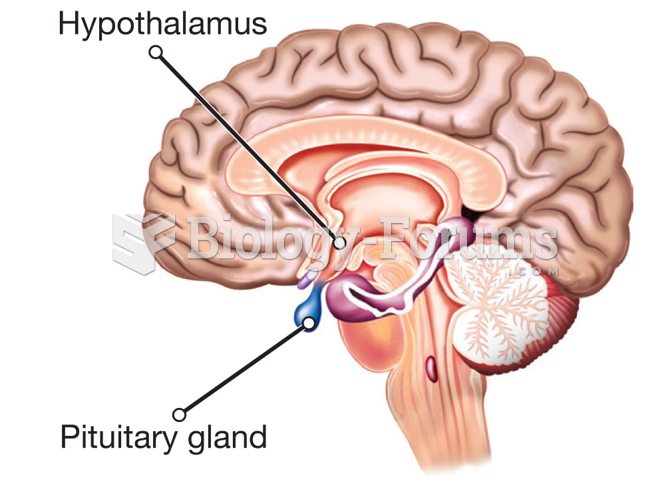
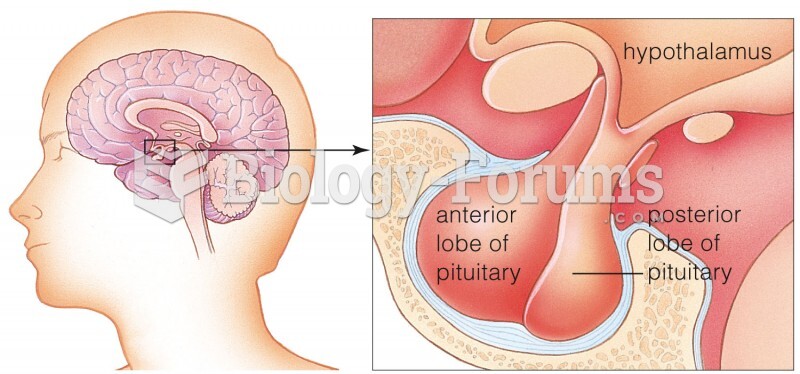
|
|
|
Egg cells are about the size of a grain of sand. They are formed inside of a female's ovaries before she is even born.
The types of cancer that alpha interferons are used to treat include hairy cell leukemia, melanoma, follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma.
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates’s recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
When Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the first mercury thermometer, he called "zero degrees" the lowest temperature he was able to attain with a mixture of ice and salt. For the upper point of his scale, he used 96°, which he measured as normal human body temperature (we know it to be 98.6° today because of more accurate thermometers).