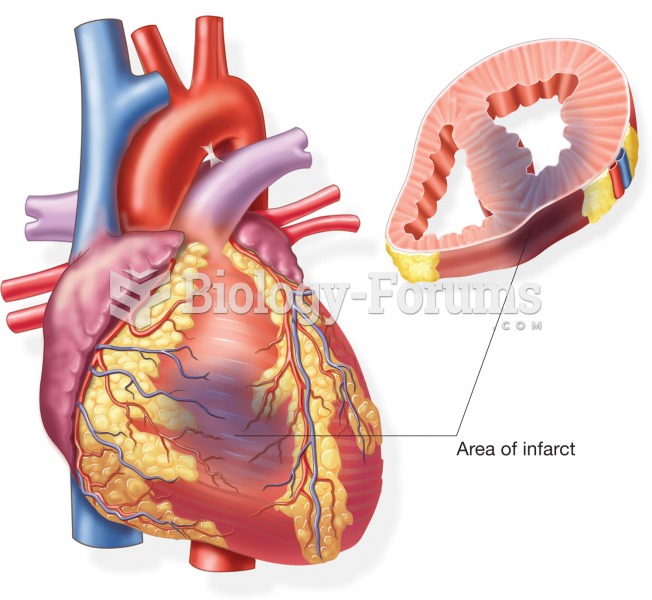
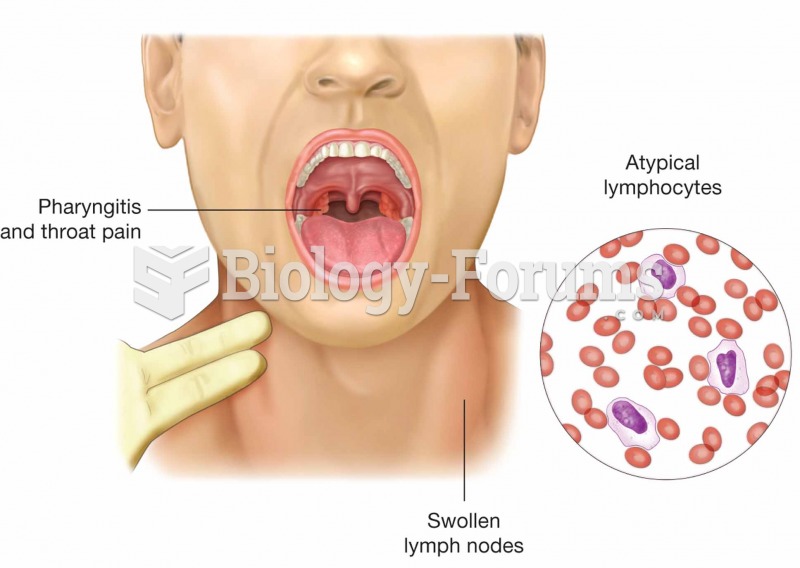
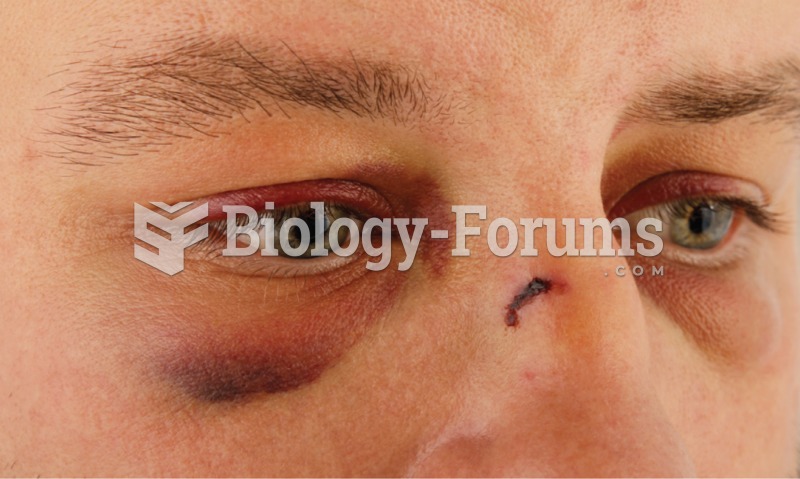
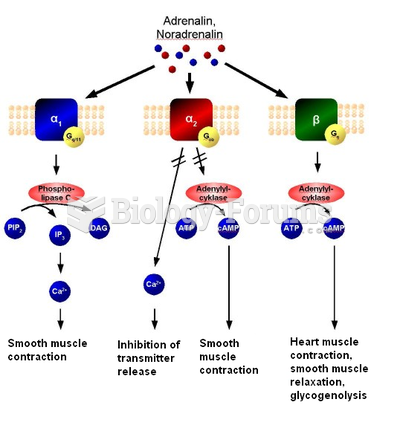
|
|
|
The training of an anesthesiologist typically requires four years of college, 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of residency.
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.