|
|
|
Side effects from substance abuse include nausea, dehydration, reduced productivitiy, and dependence. Though these effects usually worsen over time, the constant need for the substance often overcomes rational thinking.
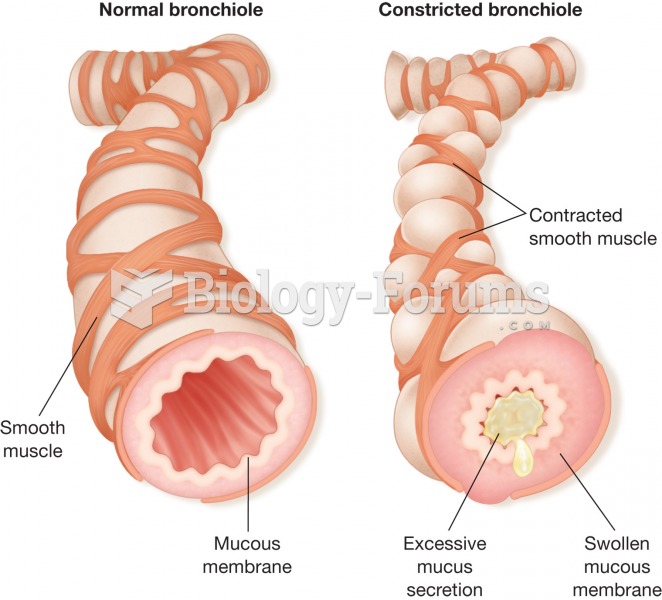
Anesthesia awareness is a potentially disturbing adverse effect wherein patients who have been paralyzed with muscle relaxants may awaken. They may be aware of their surroundings but unable to communicate or move. Neurologic monitoring equipment that helps to more closely check the patient's anesthesia stages is now available to avoid the occurrence of anesthesia awareness.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
Women are two-thirds more likely than men to develop irritable bowel syndrome. This may be attributable to hormonal changes related to their menstrual cycles.
Many supplement containers do not even contain what their labels say. There are many documented reports of products containing much less, or more, that what is listed on their labels. They may also contain undisclosed prescription drugs and even contaminants.
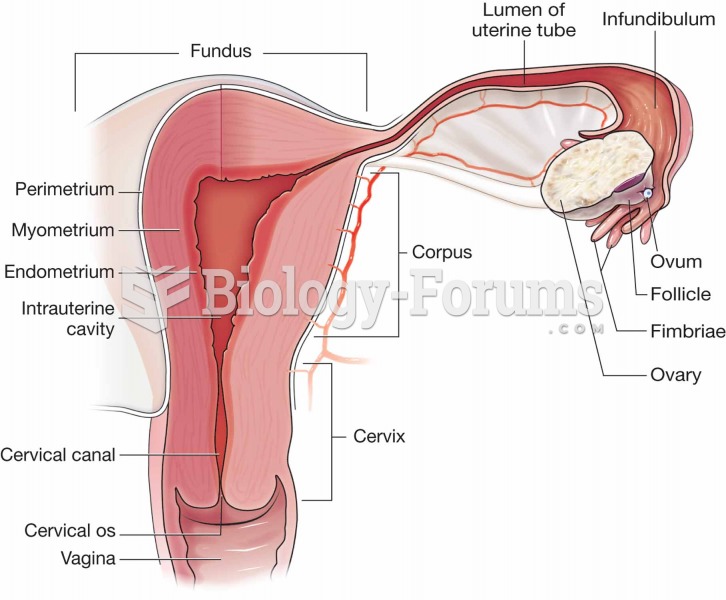
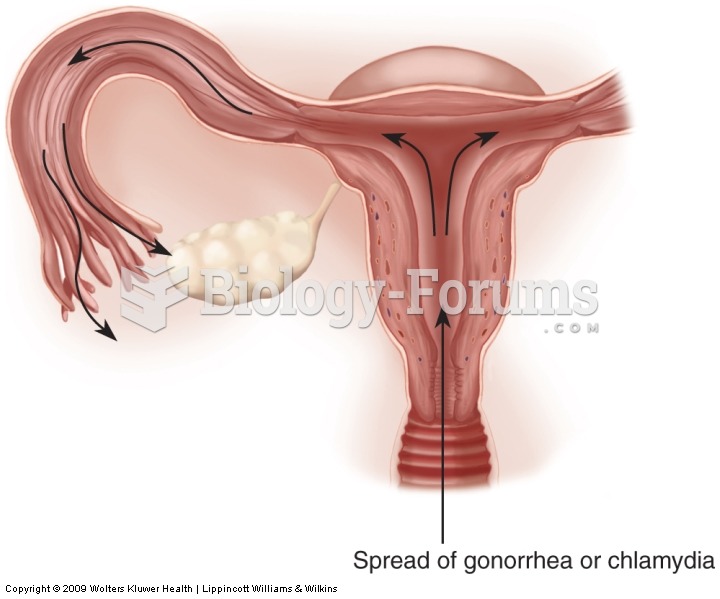 Pelvic inflammatory disease. Chlamydia or gonorrhea spreads up the vagina into the uterus and then t
Pelvic inflammatory disease. Chlamydia or gonorrhea spreads up the vagina into the uterus and then t
 Herbivores of greatly different sizes can feed upon the same plant tissues. Though here we can see t
Herbivores of greatly different sizes can feed upon the same plant tissues. Though here we can see t