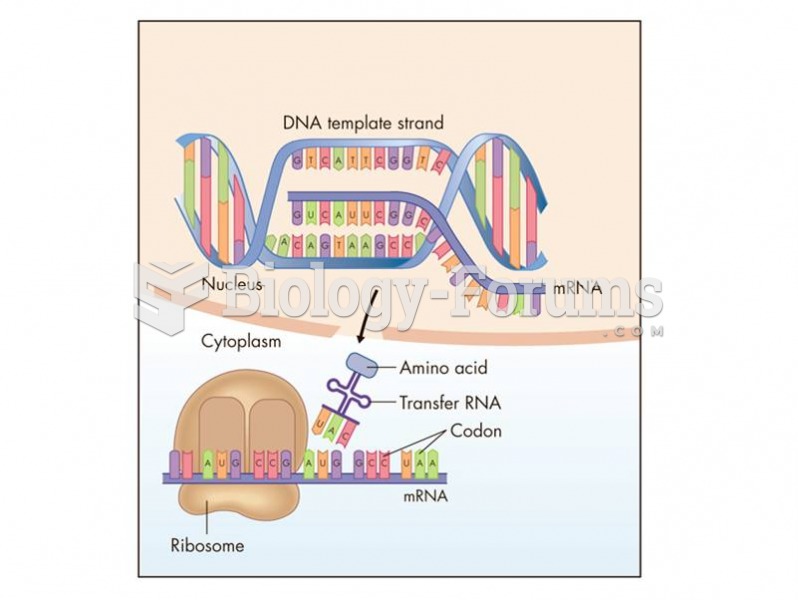
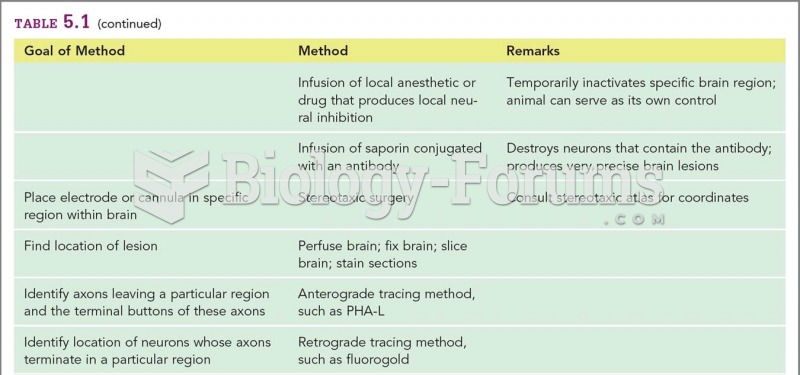
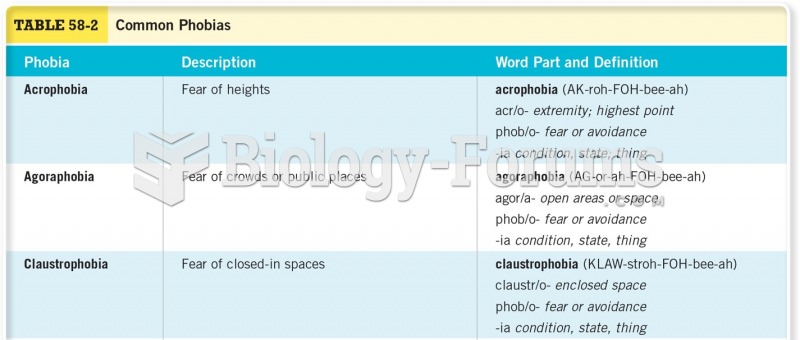
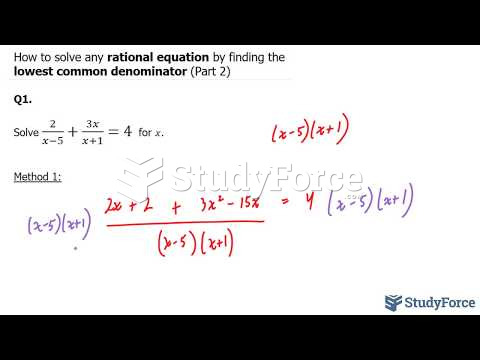
Answer to Question 1
Time: Ordering data by time means establishing a chronology of events.
Example: Ivan is preparing an agenda for next week's committee meeting.
Component: Especially for informational reports, data may be organized by components such as location, geography, division, product, or part.
Example: Olivia is preparing a report that shows sales figures for each mall tenant for December.
Importance: Organization by importance involves beginning with the most important item and proceeding to the least importantor vice versa.
Example: Leonardo is preparing a report that describes ten reasons for employee turnover. He plans to present the most common reason first, followed by less common reasons.
Criteria: Reports that compare two or more items can be arranged by criteria to help readers make comparisons.
Example: Tristan is writing a report in which he will compare three possible locations for his company's next branch location.
Convention: Many operational and recurring reports are structured using a prescribed plan that everyone understands.
Example: Catherine is a sales rep and must submit a weekly sales report to her supervisor. Each week she uses the same headings in her report.
Answer to Question 2
Conclusions: Summarize and explain the findings. Conclusions should analyze information logically and show how the data answer questions and solve problems.
Example: All employees reported finding it difficult to take care of personal obligations such as attending children's activities and medical appointments during the regular workweek because of professional obligations.
Recommendations: Make specific suggestions for actions that can solve the report problem.
Example: Investigate implementing a flexible work schedule that will allow employees options for meeting their 40-hour per week requirement and will maintain our high standards of customer care.