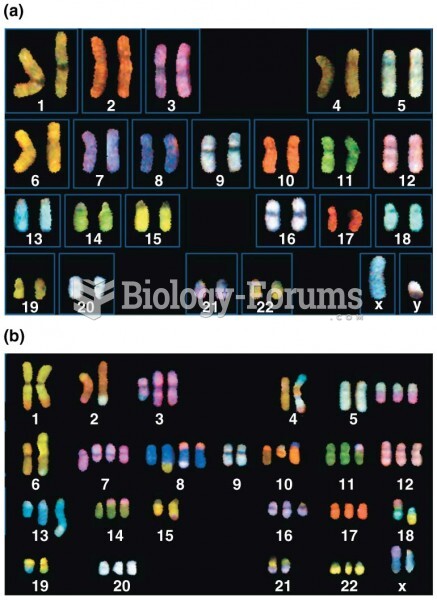
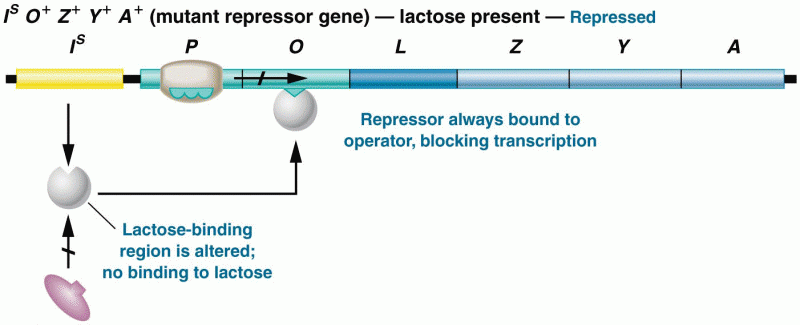
|
|
|
Did you know?
The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 and occurred in Boston. A kidney from an identical twin was transplanted into his dying brother's body and was not rejected because it did not appear foreign to his body.
Did you know?
Women are 50% to 75% more likely than men to experience an adverse drug reaction.
Did you know?
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.
Did you know?
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.
Did you know?
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.