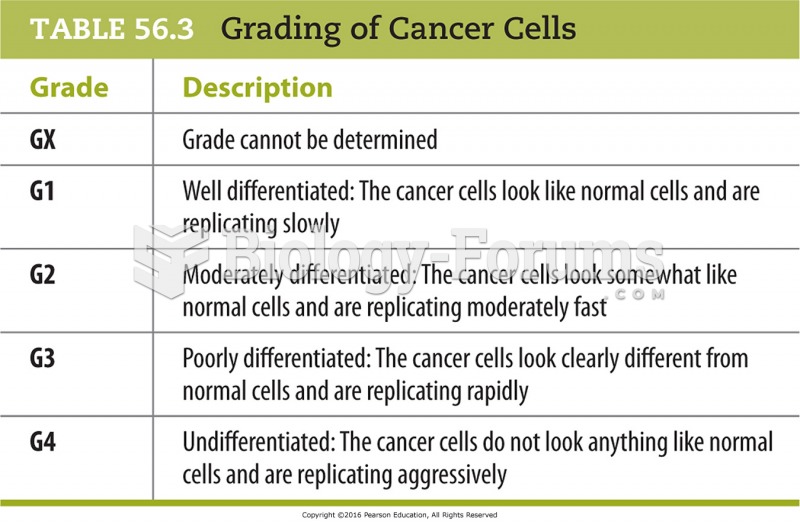
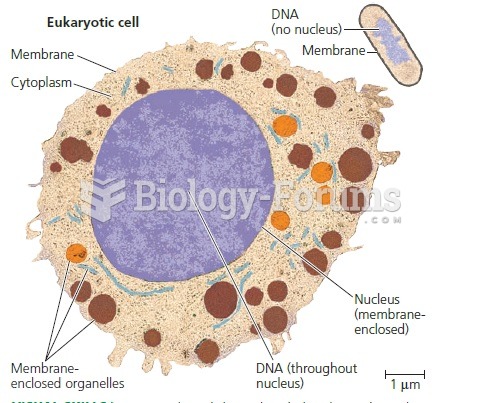
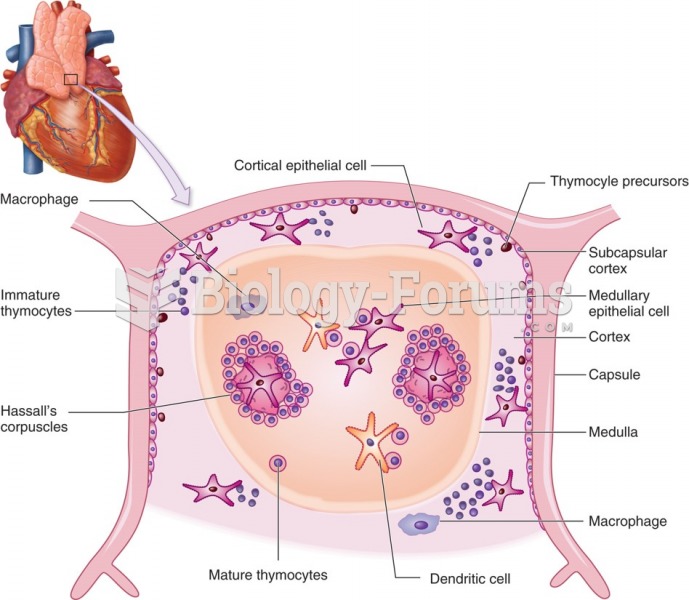
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Did you know?
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased rate of metabolism and affects about 1% of women but only 0.1% of men. For most people, this increased metabolic rate causes the thyroid gland to become enlarged (known as a goiter).
Did you know?
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
Did you know?
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Did you know?
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.