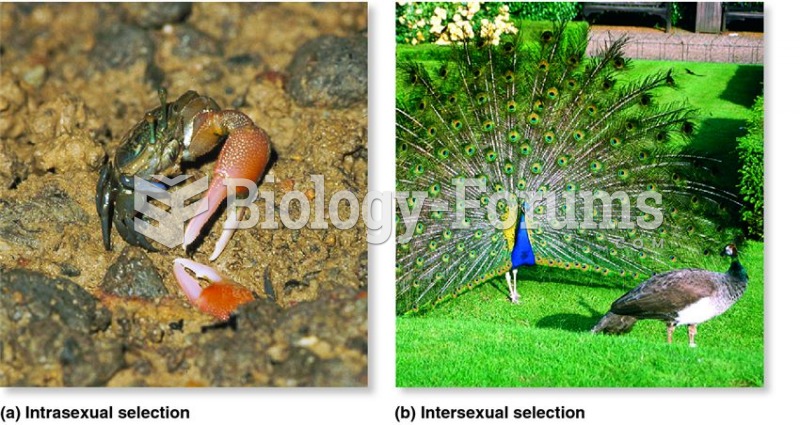
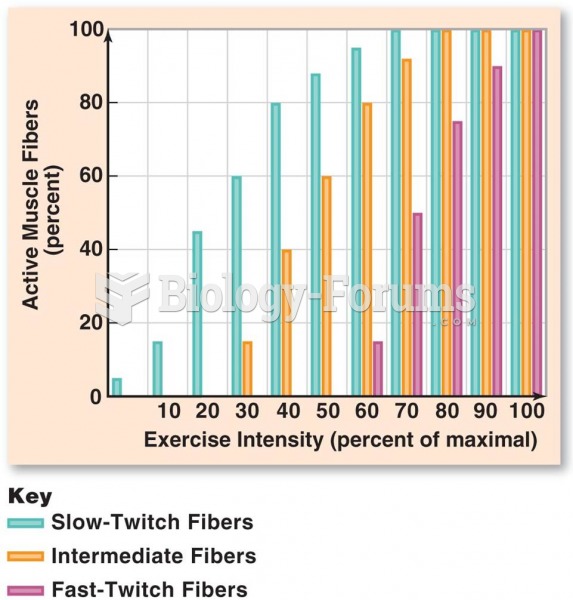
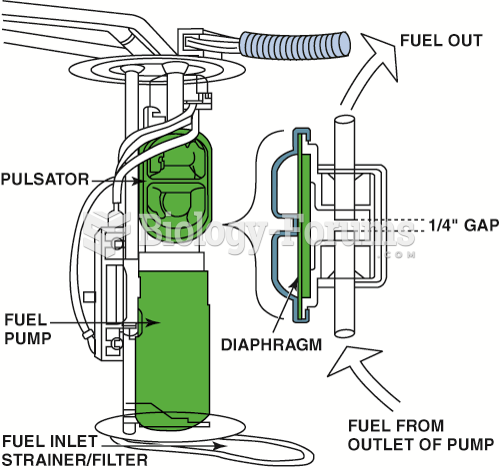
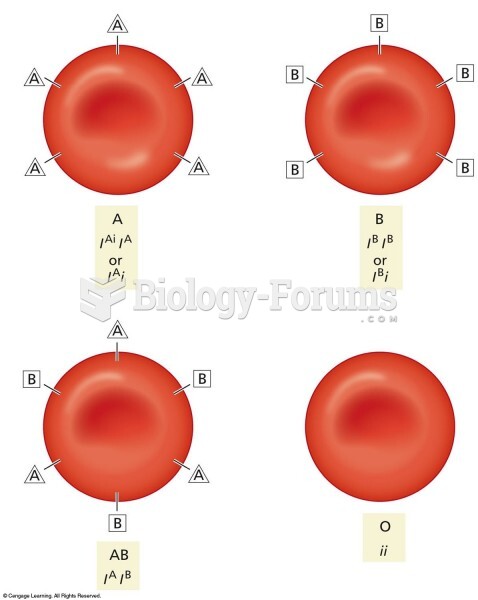
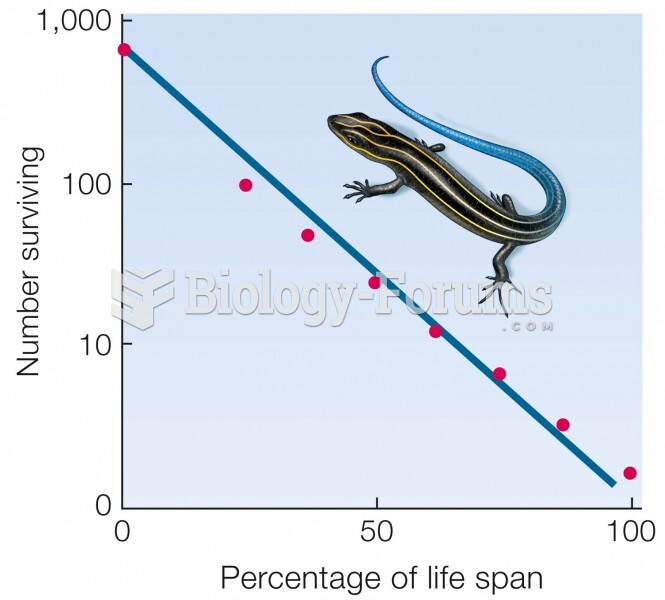
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
Did you know?
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
Did you know?
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
Did you know?
The liver is the only organ that has the ability to regenerate itself after certain types of damage. As much as 25% of the liver can be removed, and it will still regenerate back to its original shape and size. However, the liver cannot regenerate after severe damage caused by alcohol.
Did you know?
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.