Answer to Question 1
A, B, C
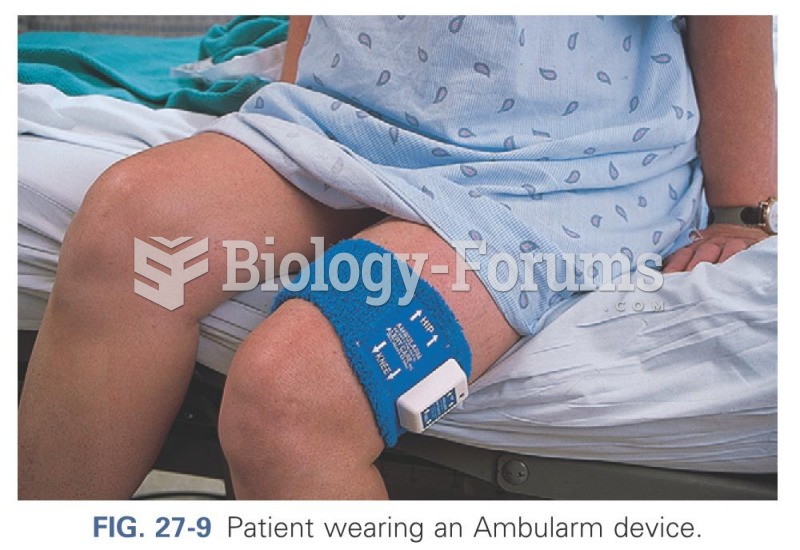
Use the following stepwise levels of interventions. Bulk-forming laxatives (e.g., psyllium Metamucil, methylcellulose Citrucel) are safe, add bulk to the fecal material, and are used in combination with a saline laxative (e.g., magnesium hydroxide milk of magnesia) or an osmotic laxative (e.g., lactulose Chronulac). The patient should increase water intake to enhance the effectiveness of bulk-forming laxatives. If constipation continues, stimulant laxatives (e.g., bisacodyl Dulcolax, senna Senokot) usually provide relief. Avoid emollient laxatives, such as mineral oil and Colace, because they are associated with lipoid aspiration pneumonia.
Answer to Question 2
A
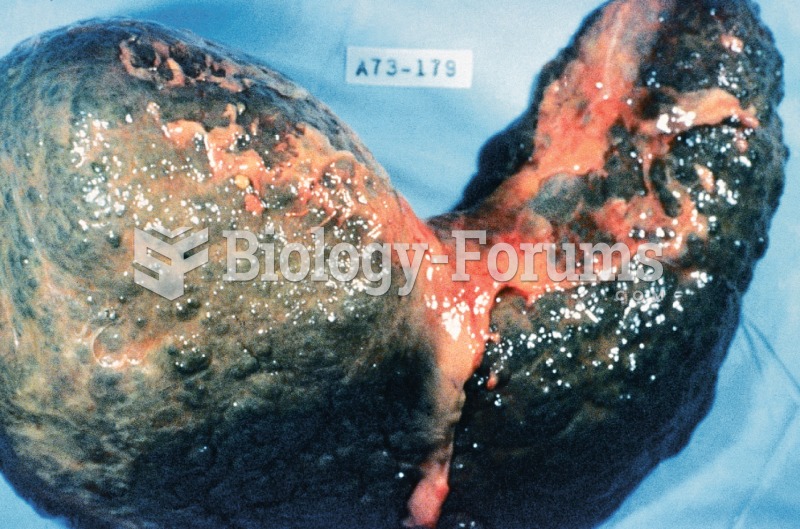
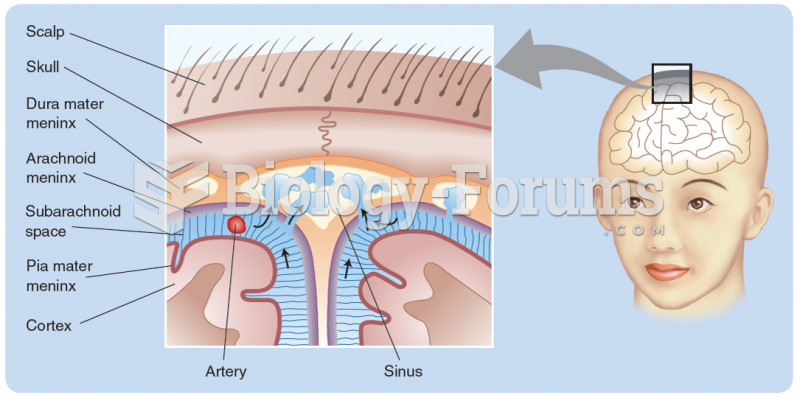
Symptoms of a delayed hemolytic reaction usually begin 2 to 14 days after the transfusion and include unexplained fever, unexplained decrease in Hgb/Hct, increased bilirubin levels, and jaundice. Symptoms of an acute hemolytic reaction usually begin within 15 minutes of transfusion initiation and include severe pain in the kidney area and chest, increased temperature (up to 105 F), increased heart rate, and increased sensation of heat and pain along the vein receiving blood, as well as chills, low back pain, headache, nausea, chest or back pain, chest tightness, dyspnea, bronchospasm, anxiety, hypotension, vascular collapse, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and possibly death. Symptoms of a nonhemolytic febrile reaction begin between 30 minutes after initiation and 6 hours after completion of transfusion and include fever greater than 1 C above baseline, flushing, chills, headache, and muscle pain; they occur most frequently in immunosuppressed patients. Symptoms of an acute severe allergic reaction usually begin within 5 to 15 minutes of initiation of transfusion and include coughing, nausea, vomiting, respiratory distress, wheezing, hypotension, loss of consciousness, and possible cardiac arrest.