|
|
|
Sperm cells are so tiny that 400 to 500 million (400,000,000–500,000,000) of them fit onto 1 tsp.
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Certain rare plants containing cyanide include apricot pits and a type of potato called cassava. Fortunately, only chronic or massive ingestion of any of these plants can lead to serious poisoning.
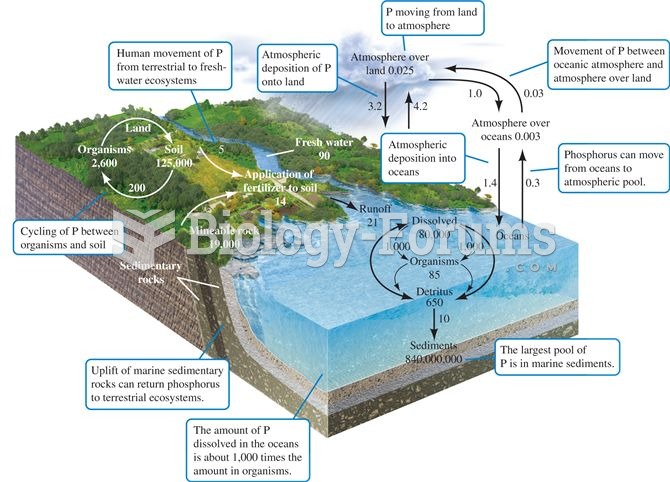 The phosphorus cycle. Numbers are 1012 g P or fluxes as 1012 g P per year (data from Schlesinger 199
The phosphorus cycle. Numbers are 1012 g P or fluxes as 1012 g P per year (data from Schlesinger 199
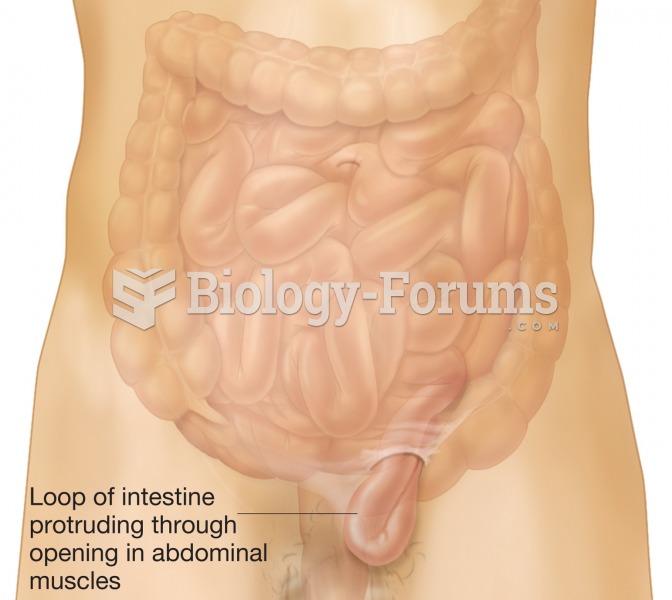 An inguinal hernia. A portion of the small intestine is protruding through the abdominal muscles int
An inguinal hernia. A portion of the small intestine is protruding through the abdominal muscles int