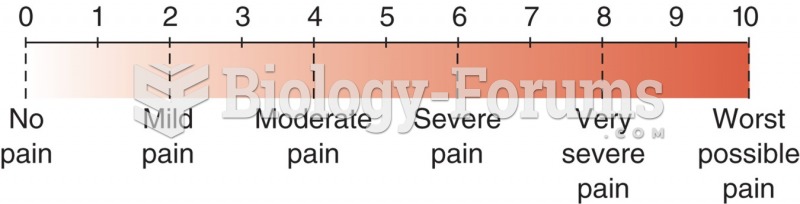
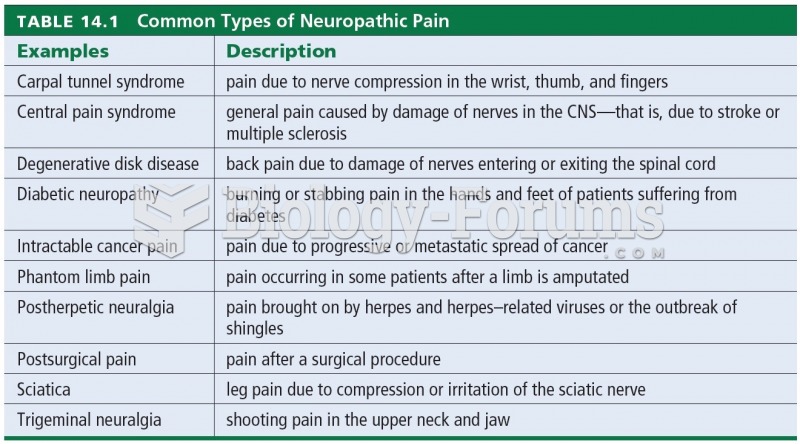
|
|
|
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
Lower drug doses for elderly patients should be used first, with titrations of the dose as tolerated to prevent unwanted drug-related pharmacodynamic effects.
Long-term mental and physical effects from substance abuse include: paranoia, psychosis, immune deficiencies, and organ damage.
The top 10 most important tips that will help you grow old gracefully include (1) quit smoking, (2) keep your weight down, (3) take supplements, (4) skip a meal each day or fast 1 day per week, (5) get a pet, (6) get medical help for chronic pain, (7) walk regularly, (8) reduce arguments, (9) put live plants in your living space, and (10) do some weight training.
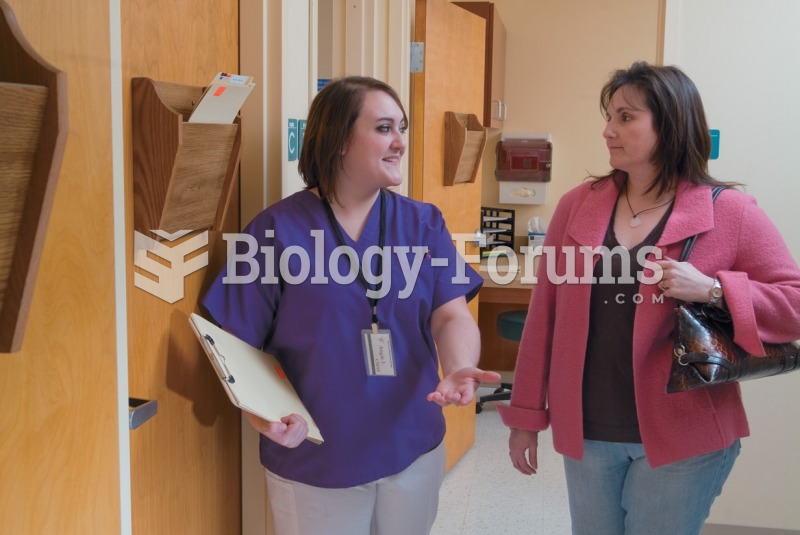
Computer programs are available that crosscheck a new drug's possible trade name with all other trade names currently available. These programs detect dangerous similarities between names and alert the manufacturer of the drug.