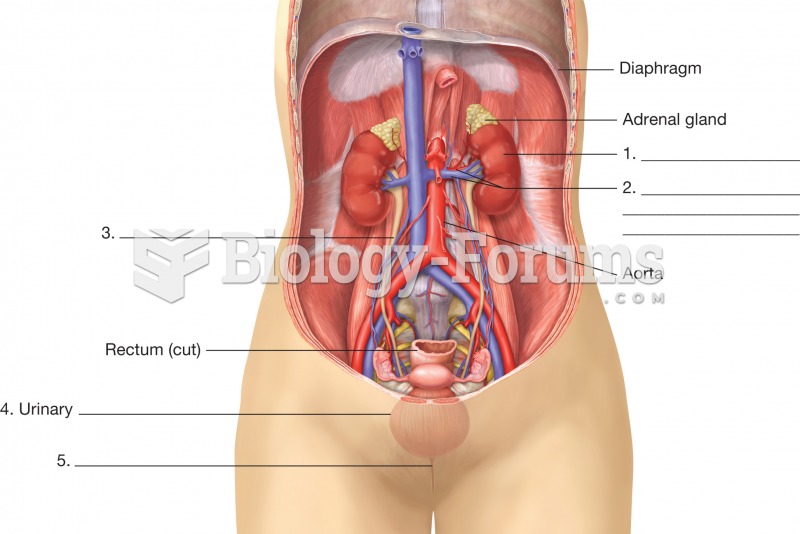
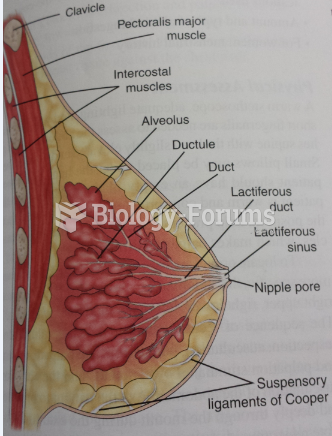
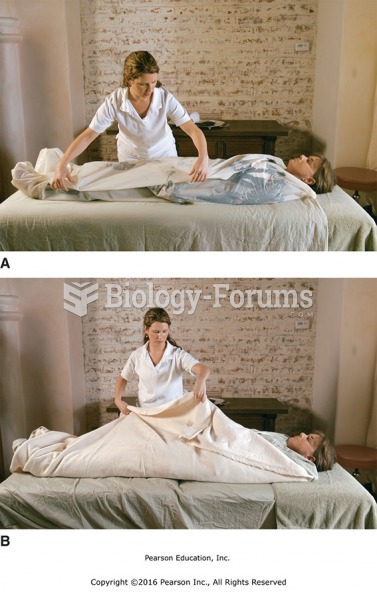
|
|
|
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
A cataract is a clouding of the eyes' natural lens. As we age, some clouding of the lens may occur. The first sign of a cataract is usually blurry vision. Although glasses and other visual aids may at first help a person with cataracts, surgery may become inevitable. Cataract surgery is very successful in restoring vision, and it is the most frequently performed surgery in the United States.