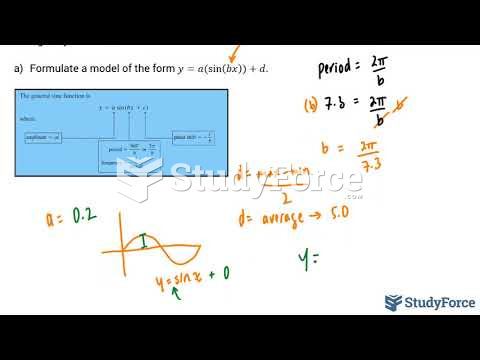
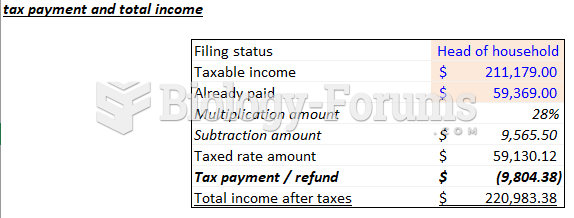
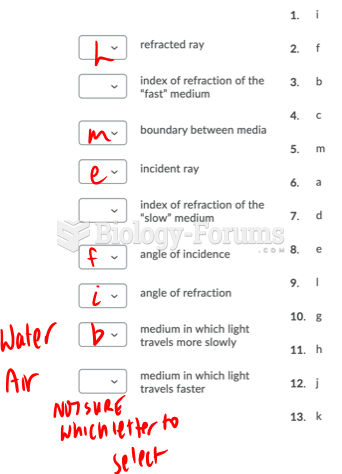
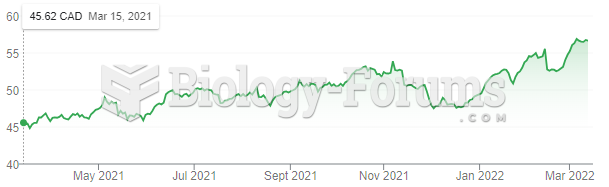
Answer to Question 1
The core software used to manage fulfillment processes is called warehouse management systems (WMS), a mature technology dating back to the 1970s. Widely used to support all types of distribution operations, WMS is a software control system that improves product movement and storage operations through efficient management of information and completion of distribution tasks. The goal is to achieve a high level of control, inventory accuracy, and productivity through directed picking, directed replenishment, and directed put-away.
A WMS is more than a simple database that provides stock location information. Instead, it is an integrated package whose components often include radio-frequency (RF) communications, dedicated localized computer hardware, and the necessary applications software. The detailed setup and processing within a WMS can vary significantly from one software vendor to another; however, the basic logic will use a combination of item, location, quantity, unit of measure, and order information to determine where to stock, where to pick, and in what sequence to perform these operations.
Beyond the main functionalities, WMS can also provide value-added capabilities and support a variety of supply chain activities. Advanced systems generate performance reports; support paperless processes; enable integration of materials-handling equipment, picking systems, and sorting systems; leverage wireless communication tools; and support automatic identification equipment data collection. Other value-added capabilities include the following:
Labor managementThe ability to link WMS with a related labor tracking module allows the organization to create assignments based on engineered time standards, monitor the productivity of each employee, and audit the quality of their work. These labor-reporting capabilities support performance analysis and the use of incentive programs, and they help identify employees in need of additional training.
Task interleavingThis process involves mixing dissimilar tasks such as put-away and replenishment. In large warehouses, WMS-based task interleaving can greatly reduce travel time, not only increasing productivity but also reducing wear on the lift trucks and saving on energy costs by reducing lift truck fuel consumption.
Systems integrationthe ability to interface the WMS with the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, order management systems, and transportation management will provide a strong flow of information across the organization and the supply chain. Inventory availability, order status, advanced shipping notification, and delivery tracking are a few of the critical visibility benefits created by integration. This shared information can be used for distribution planning purposes.
Activity-based costing/billingFinancial functionality is an important WMS capability for understanding costs and assigning expenses to distribution customers. Primarily designed for 3PL operations, activity-based billing allows them to calculate billable fees based on specific activities. For example, 3PL providers can assign transaction fees for each receipt and shipment transaction, as well as fees for storage and other value-added activities.
Multifunction distributionA strong WMS will support a variety of distribution methods, shipment sizes, and the execution of value-added services. The ability to support traditional case pick distribution and cross-docking, retailer orders and individual consumer orders, and light assembly and kitting operations creates flexibility for the distribution operation and the supply chain.
Improved productivity, efficiency, and accuracy are key WMS benefits. By keeping track of item locations in the facility, the WMS reduces wasted efforts associated with warehouse personnel hunting for an item. This improves labor productivity, reduces the number of personnel required, and improves the order-picking accuracy. The WMS also provides essential information that enables businesses to quickly make accurate decisions that are based on up-to-date information. In addition, these systems improve space utilization by determining the optimal storage patterns to maximize space utilization. Finally, the WMS provides improved managerial control and effectiveness through point-of-work confirmation, accountability, performance measurement, and what-if scenario planning.
Answer to Question 2
c