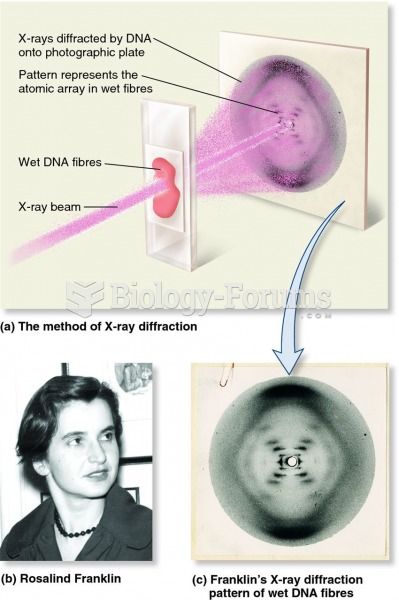
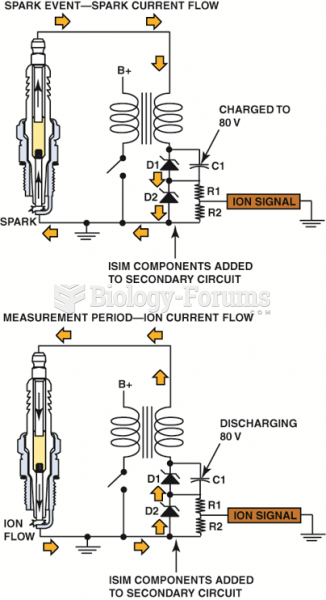
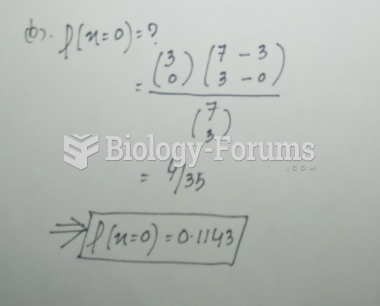|
|
|
The largest baby ever born weighed more than 23 pounds but died just 11 hours after his birth in 1879. The largest surviving baby was born in October 2009 in Sumatra, Indonesia, and weighed an astounding 19.2 pounds at birth.
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
Approximately one in three babies in the United States is now delivered by cesarean section. The number of cesarean sections in the United States has risen 46% since 1996.
Pink eye is a term that refers to conjunctivitis, which is inflammation of the thin, clear membrane (conjunctiva) over the white part of the eye (sclera). It may be triggered by a virus, bacteria, or foreign body in the eye. Antibiotic eye drops alleviate bacterial conjunctivitis, and antihistamine allergy pills or eye drops help control allergic conjunctivitis symptoms.
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness. As of yet, there is no cure. Everyone is at risk, and there may be no warning signs. It is six to eight times more common in African Americans than in whites. The best and most effective way to detect glaucoma is to receive a dilated eye examination.