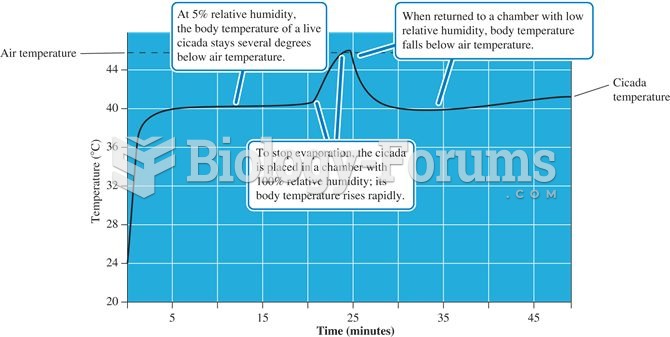
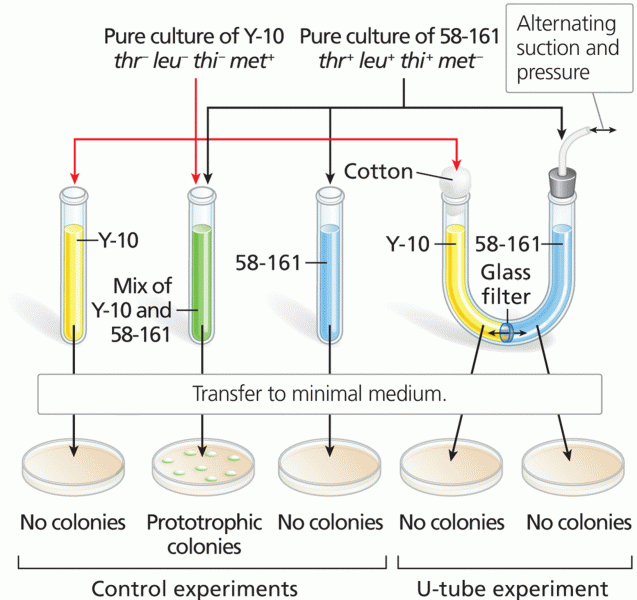
|
|
|
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.
Eating food that has been cooked with poppy seeds may cause you to fail a drug screening test, because the seeds contain enough opiate alkaloids to register as a positive.