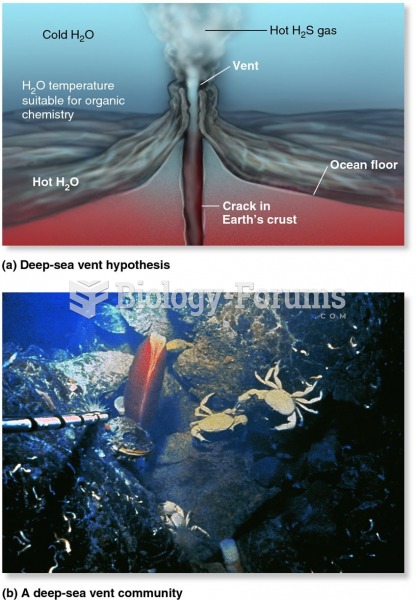
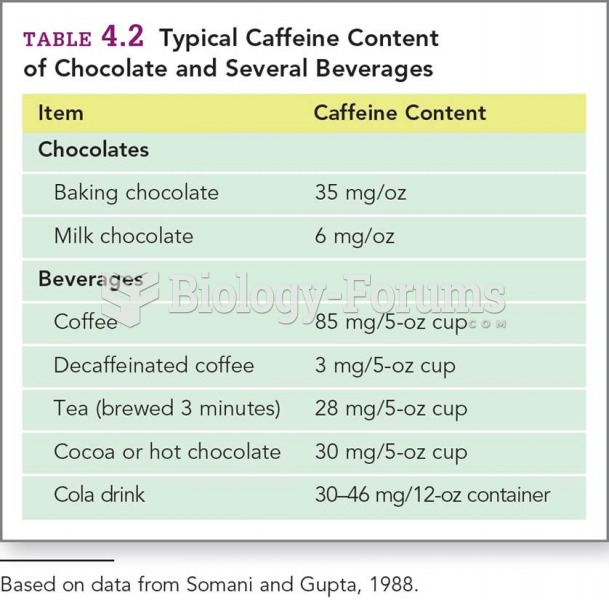
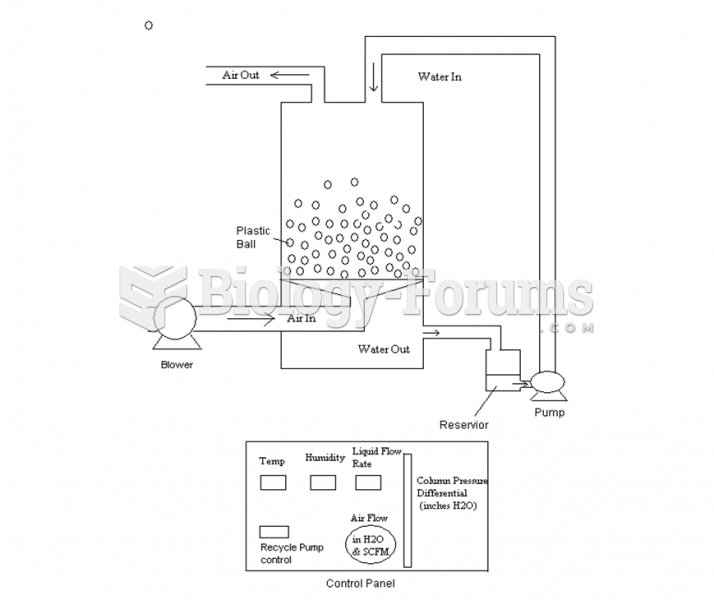
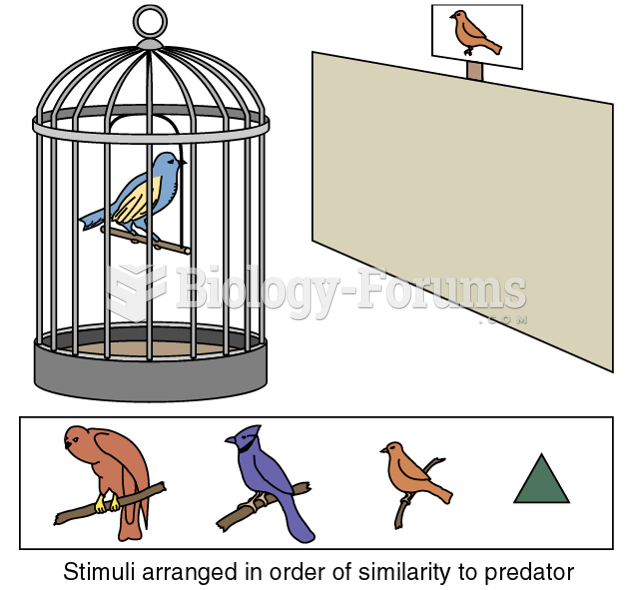
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
Did you know?
There are more sensory neurons in the tongue than in any other part of the body.
Did you know?
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
Did you know?
Children of people with alcoholism are more inclined to drink alcohol or use hard drugs. In fact, they are 400 times more likely to use hard drugs than those who do not have a family history of alcohol addiction.
Did you know?
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.