|
|
|
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.
Astigmatism is the most common vision problem. It may accompany nearsightedness or farsightedness. It is usually caused by an irregularly shaped cornea, but sometimes it is the result of an irregularly shaped lens. Either type can be corrected by eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.
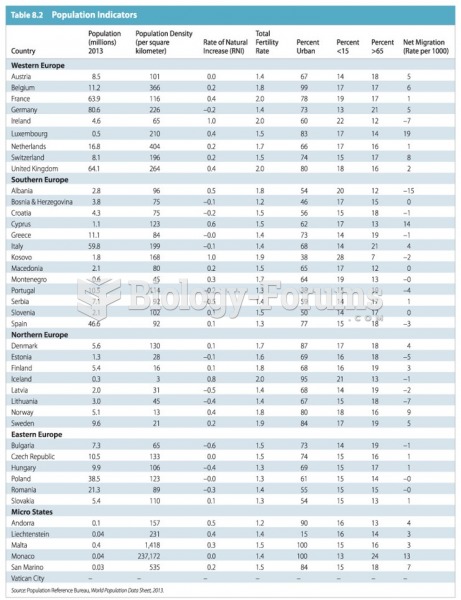
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.