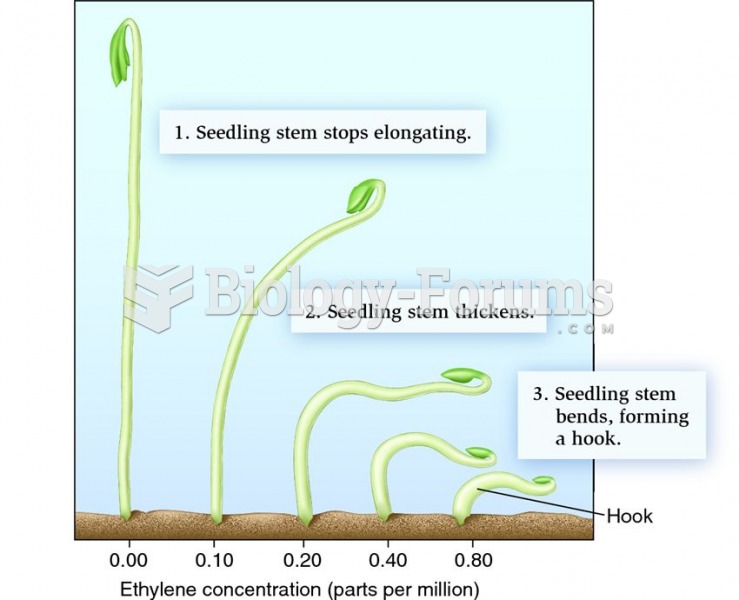
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
Did you know?
In 2010, opiate painkllers, such as morphine, OxyContin®, and Vicodin®, were tied to almost 60% of drug overdose deaths.
Did you know?
Multiple sclerosis is a condition wherein the body's nervous system is weakened by an autoimmune reaction that attacks the myelin sheaths of neurons.
Did you know?
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Did you know?
About 600,000 particles of skin are shed every hour by each human. If you live to age 70 years, you have shed 105 pounds of dead skin.