|
|
|
An identified risk factor for osteoporosis is the intake of excessive amounts of vitamin A. Dietary intake of approximately double the recommended daily amount of vitamin A, by women, has been shown to reduce bone mineral density and increase the chances for hip fractures compared with women who consumed the recommended daily amount (or less) of vitamin A.
The largest baby ever born weighed more than 23 pounds but died just 11 hours after his birth in 1879. The largest surviving baby was born in October 2009 in Sumatra, Indonesia, and weighed an astounding 19.2 pounds at birth.
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
There are more nerve cells in one human brain than there are stars in the Milky Way.
In 1864, the first barbiturate (barbituric acid) was synthesized.
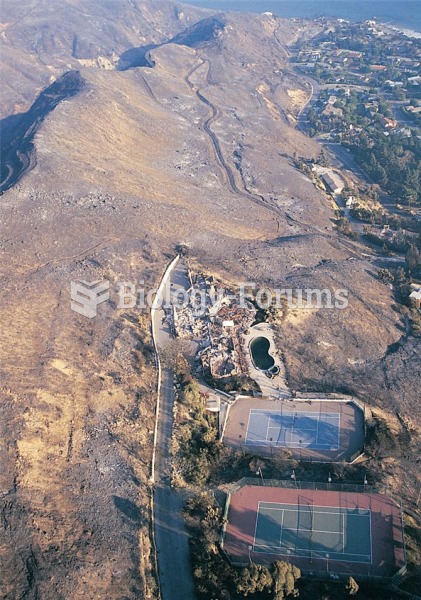 Areas of Mediterranean shrubland in southern California periodically burn over large areas, destroyi
Areas of Mediterranean shrubland in southern California periodically burn over large areas, destroyi
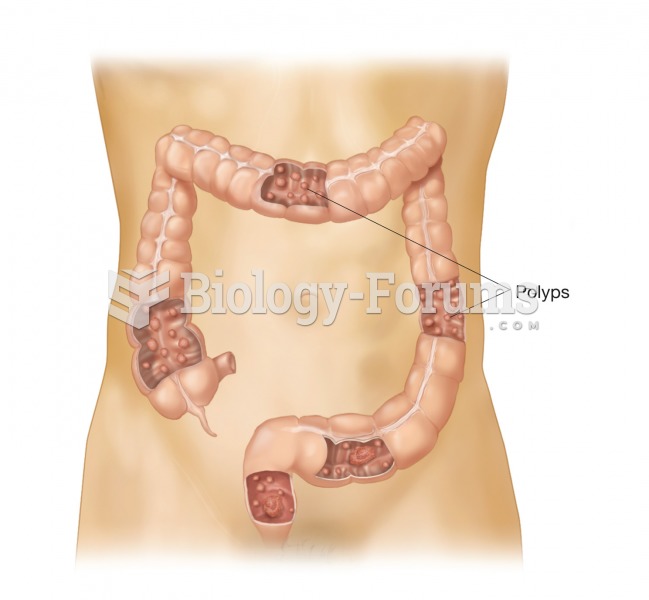 Polyps and polyposis. A polyp is a protruding growth from a mucous membrane lining a hollow organ. I
Polyps and polyposis. A polyp is a protruding growth from a mucous membrane lining a hollow organ. I





